5.9 KiB
| title |
|---|
| Using Logger - Jupyter Notebook |
The jupyter_logging_example.ipynb
script demonstrates the integration of ClearML's explicit reporting module, Logger, in a Jupyter Notebook. All ClearML
explicit reporting works with Jupyter Notebook.
This example includes several types of explicit reporting, including:
- Scalars
- Some plots
- Media.
:::note
In the clearml GitHub repository, this example includes a clickable icon to open the notebook in Google Colab.
:::
Scalars
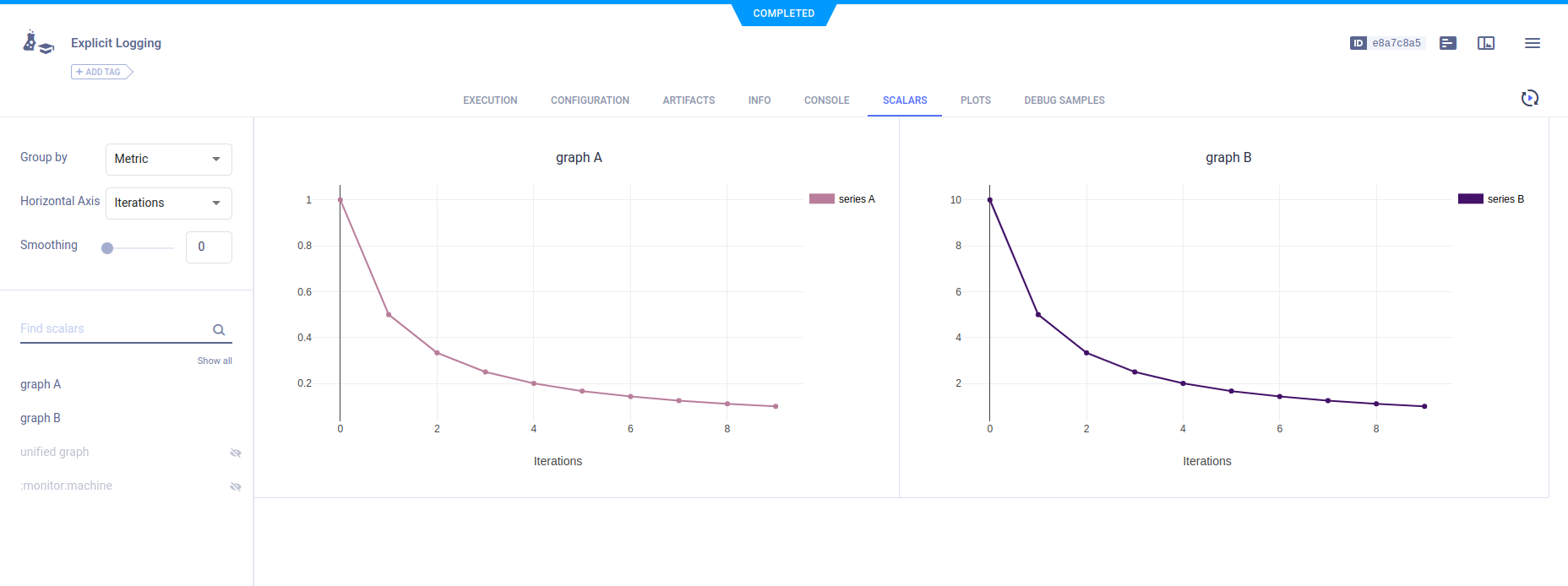
To reports scalars, call the Logger.report_scalar method. The scalar plots appear in the web UI in SCALARS.
# report two scalar series on two different graphs
for i in range(10):
logger.report_scalar("graph A", "series A", iteration=i, value=1./(i+1))
logger.report_scalar("graph B", "series B", iteration=i, value=10./(i+1))
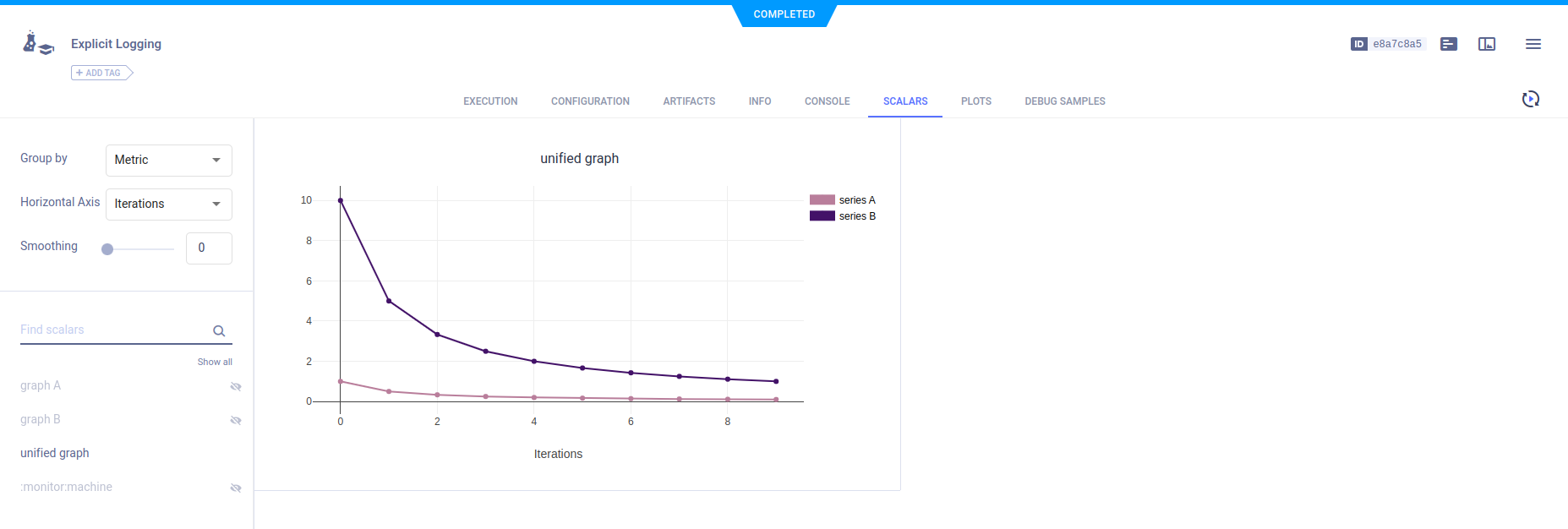
# report two scalar series on the same graph
for i in range(10):
logger.report_scalar("unified graph", "series A", iteration=i, value=1./(i+1))
logger.report_scalar("unified graph", "series B", iteration=i, value=10./(i+1))
Plots
Plots appear in PLOTS.
2D Plots
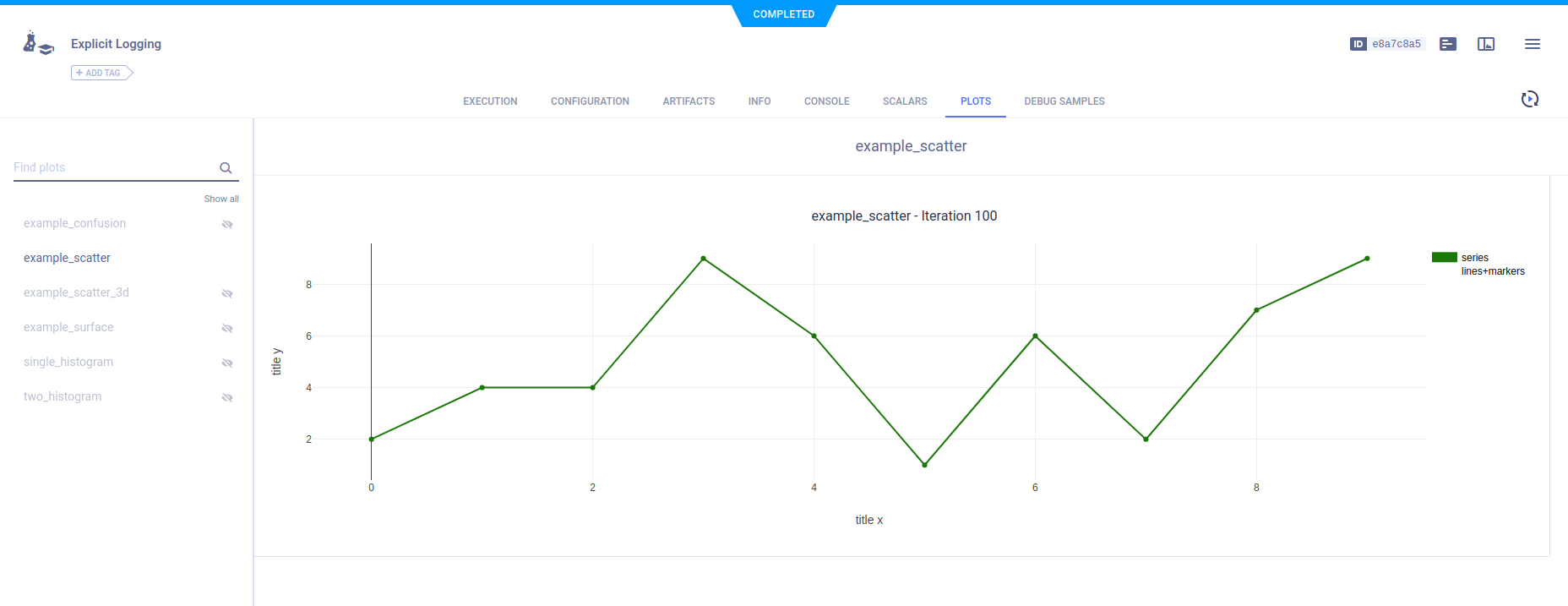
Report 2D scatter plots by calling the Logger.report_scatter2d method.
Use the mode parameter to plot data points as markers, or both lines and markers.
scatter2d = np.hstack(
(np.atleast_2d(np.arange(0, 10)).T, np.random.randint(10, size=(10, 1)))
)
# report 2d scatter plot with markers
logger.report_scatter2d(
"example_scatter",
"series_lines+markers",
iteration=iteration,
scatter=scatter2d,
xaxis="title x",
yaxis="title y",
mode='lines+markers'
)
3D Plots
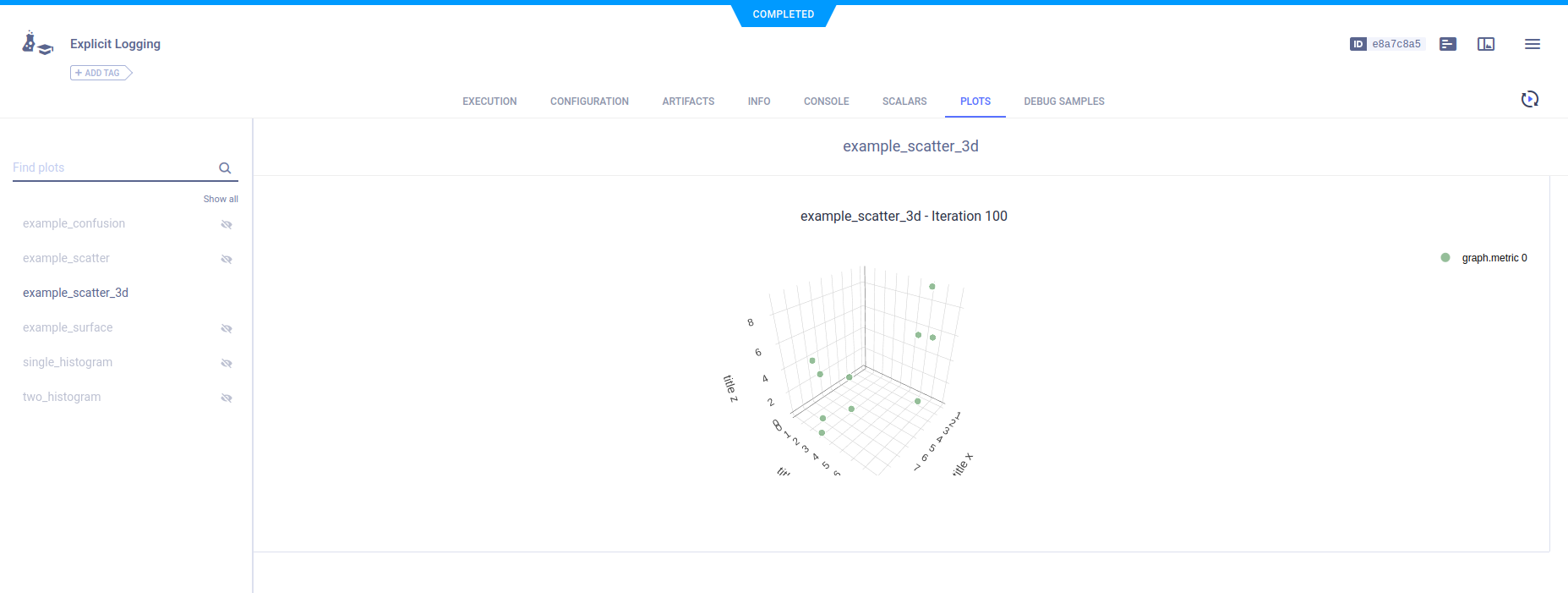
To plot a series as a 3D scatter plot, use the Logger.report_scatter3d method.
# report 3d scatter plot
scatter3d = np.random.randint(10, size=(10, 3))
logger.report_scatter3d(
"example_scatter_3d",
"series_xyz",
iteration=iteration,
scatter=scatter3d,
xaxis="title x",
yaxis="title y",
zaxis="title z",
)
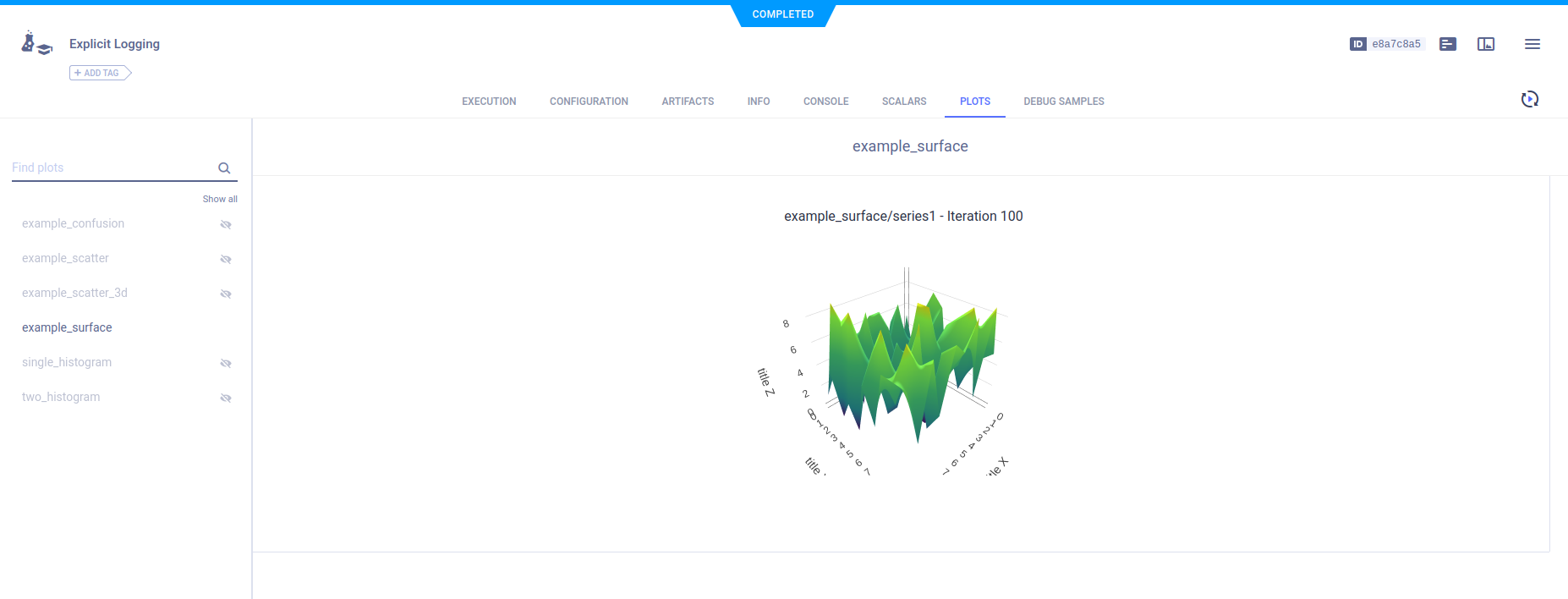
To plot a series as a surface plot, use the Logger.report_surface method.
# report 3d surface
surface = np.random.randint(10, size=(10, 10))
logger.report_surface(
"example_surface",
"series1",
iteration=iteration,
matrix=surface,
xaxis="title X",
yaxis="title Y",
zaxis="title Z",
)
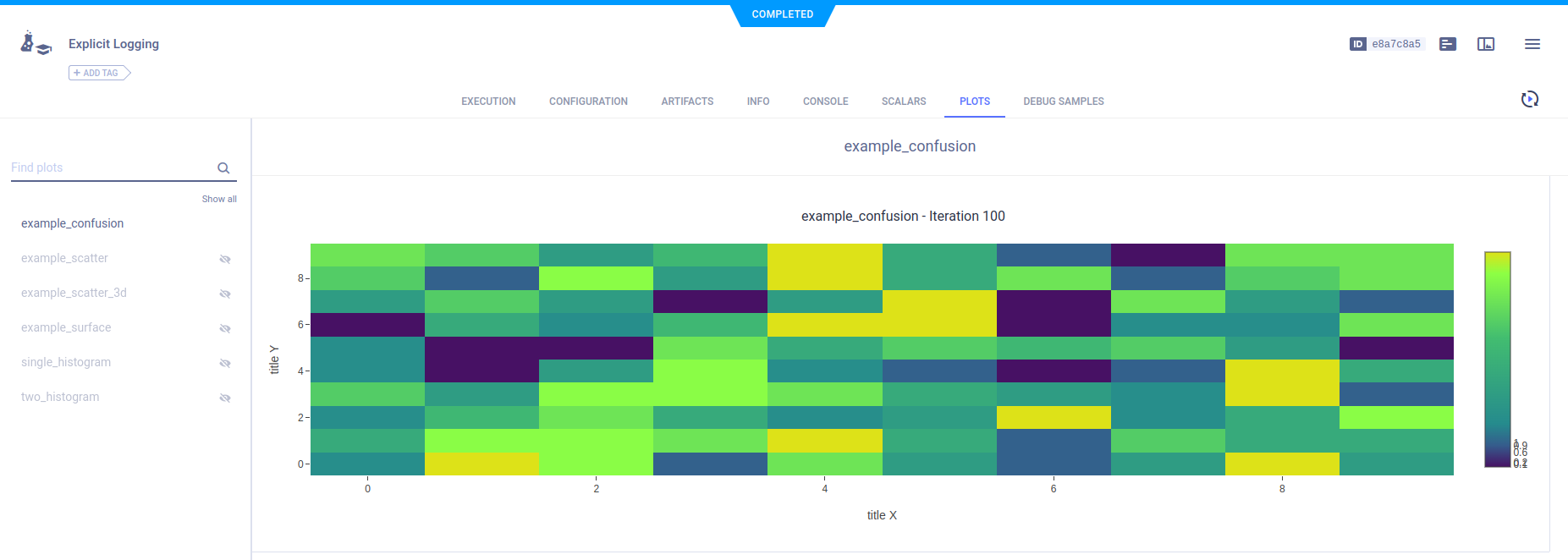
Confusion Matrices
Report confusion matrices by calling Logger.report_confusion_matrix().
# report confusion matrix
confusion = np.random.randint(10, size=(10, 10))
logger.report_confusion_matrix(
"example_confusion",
"ignored",
iteration=iteration,
matrix=confusion,
xaxis="title X",
yaxis="title Y",
)
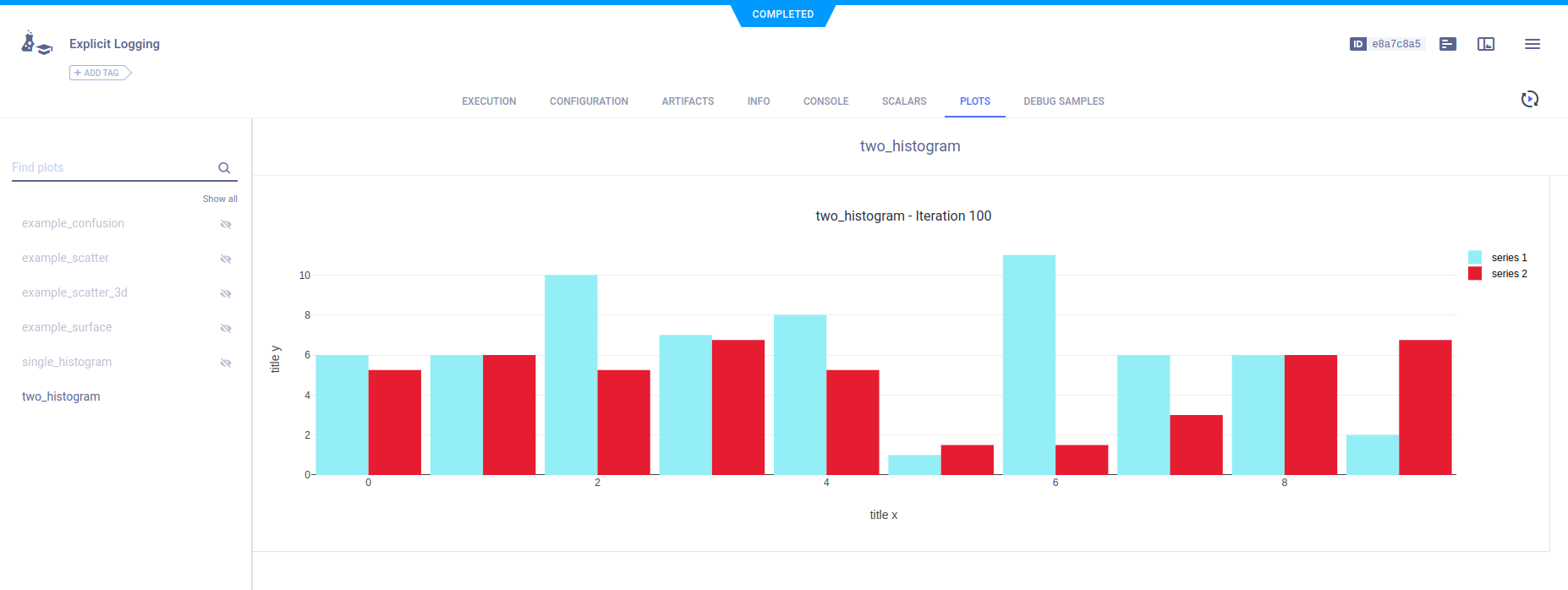
Histograms
Report histograms by calling Logger.report_histogram().
To report more than one series on the same plot, use the same title argument.
# report a single histogram
histogram = np.random.randint(10, size=10)
logger.report_histogram(
"single_histogram",
"random histogram",
iteration=iteration,
values=histogram,
xaxis="title x",
yaxis="title y",
)
# report a two histograms on the same plot
histogram1 = np.random.randint(13, size=10)
histogram2 = histogram * 0.75
logger.report_histogram(
"two_histogram",
"series 1",
iteration=iteration,
values=histogram1,
xaxis="title x",
yaxis="title y",
)
logger.report_histogram(
"two_histogram",
"series 2",
iteration=iteration,
values=histogram2,
xaxis="title x",
yaxis="title y",
)
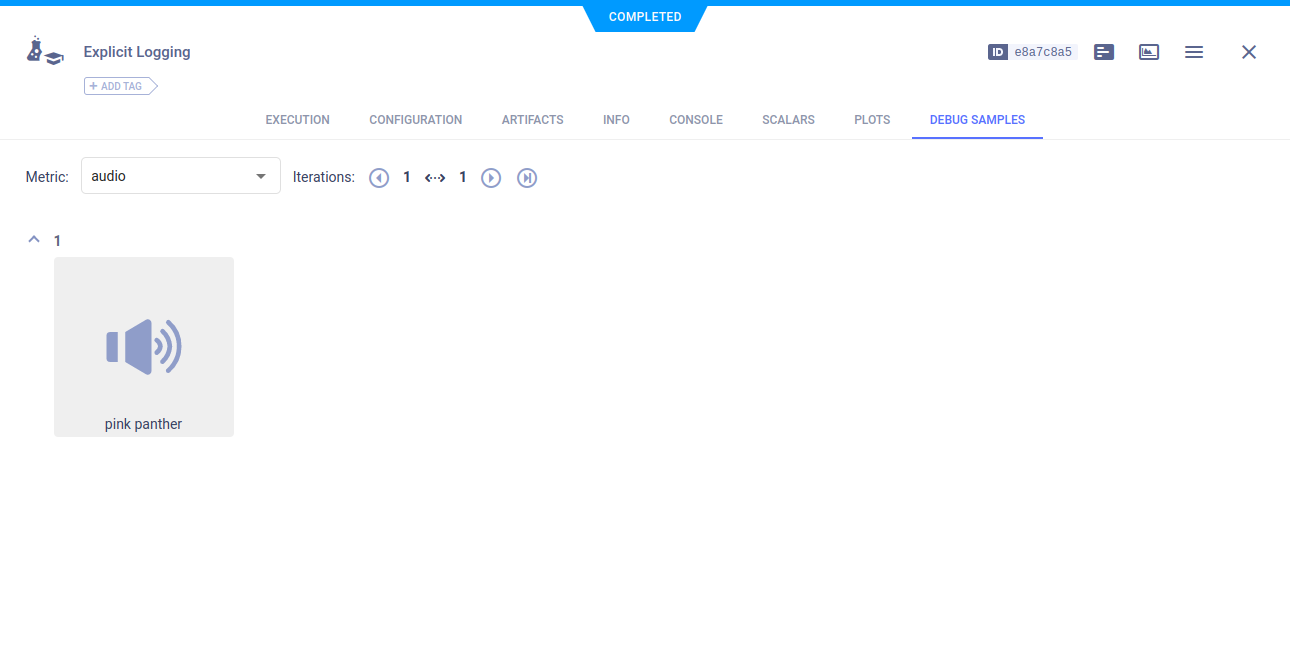
Media
Report audio, HTML, image, and video by calling Logger.report_media()
using the local_path parameter. They appear in DEBUG SAMPLES.
The media for these examples is downloaded using StorageManager.get_local_copy().
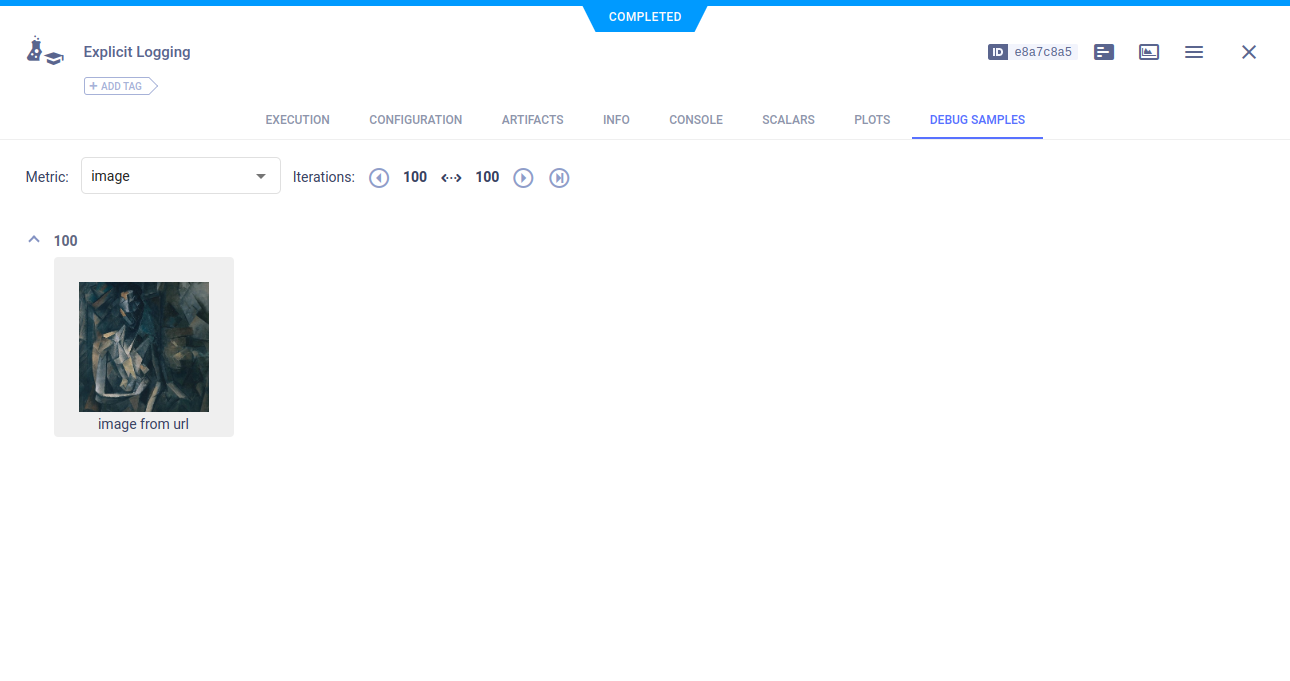
For example, to download an image:
image_local_copy = StorageManager.get_local_copy(
remote_url="https://pytorch.org/tutorials/_static/img/neural-style/picasso.jpg",
name="picasso.jpg"
)
Audio
logger.report_media('audio', 'pink panther', iteration=1, local_path=audio_local_copy)
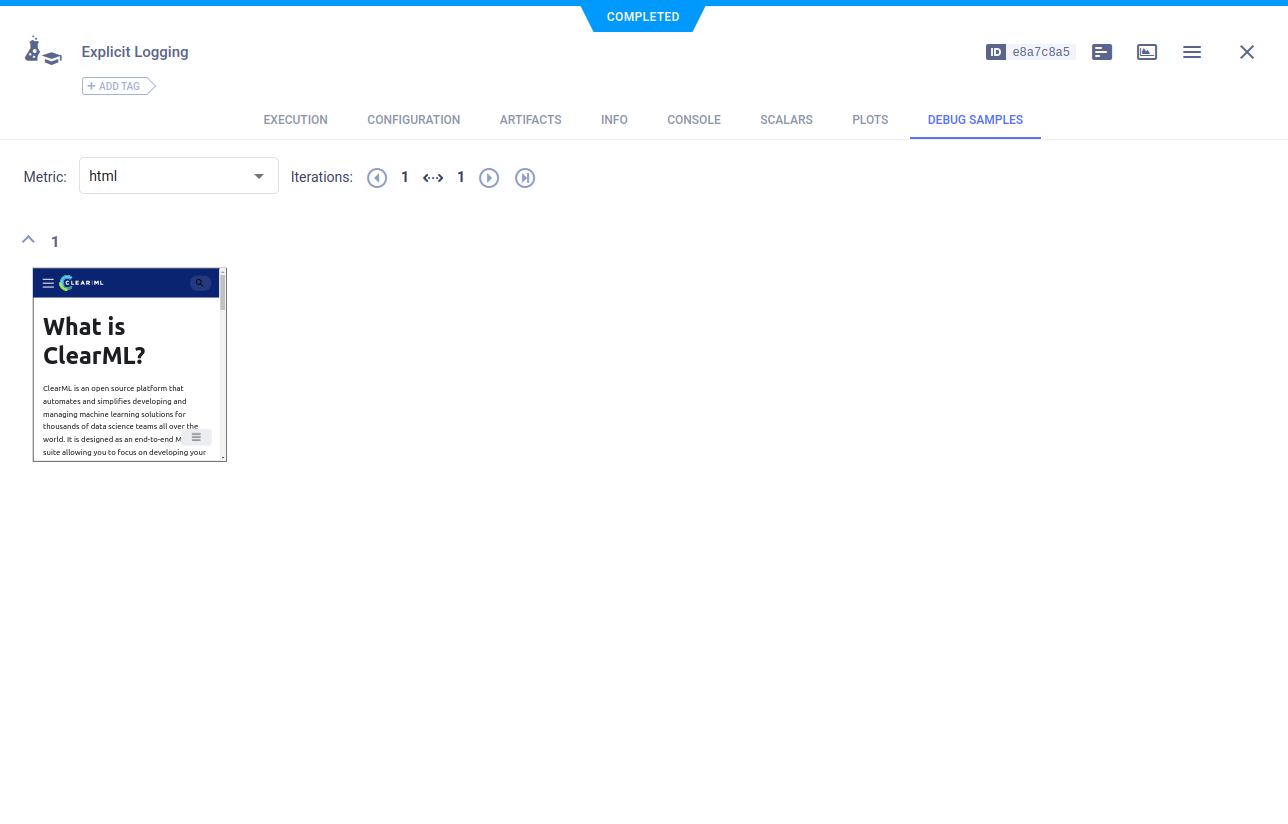
HTML
logger.report_media(
"html",
"url_html",
iteration=1,
url="https://clear.ml/docs/latest/docs/index.html"
)
Images
logger.report_image("image", "image from url", iteration=100, local_path=image_local_copy)
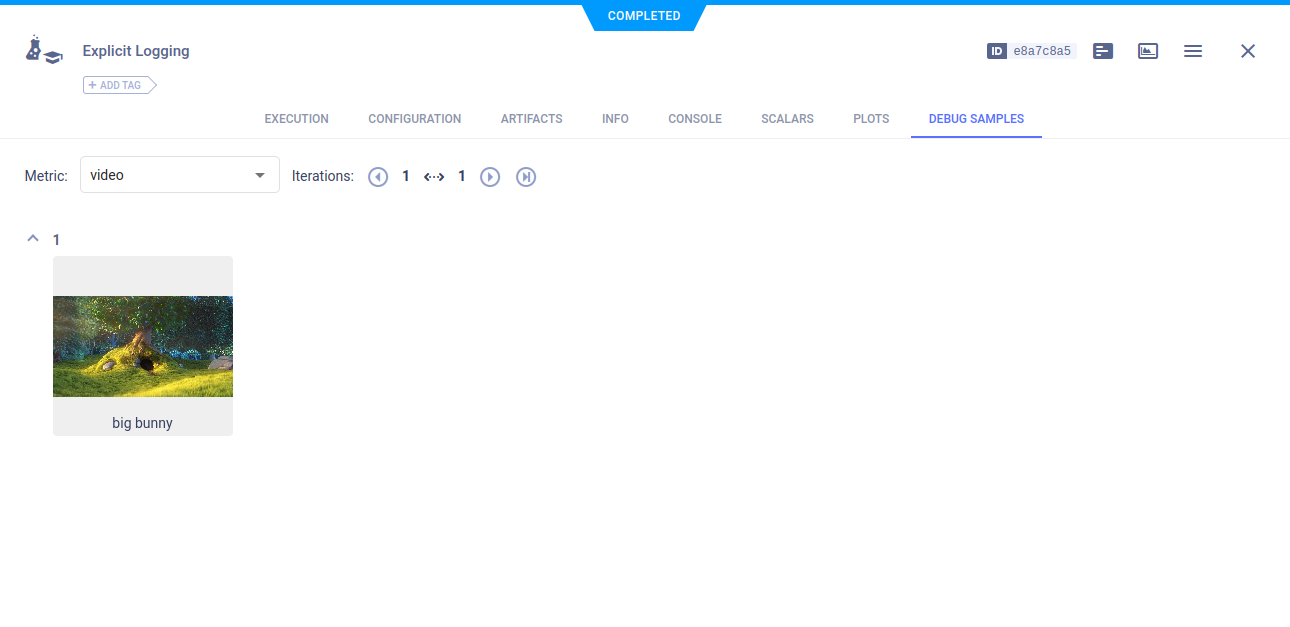
Video
logger.report_media('video', 'big bunny', iteration=1, local_path=video_local_copy)
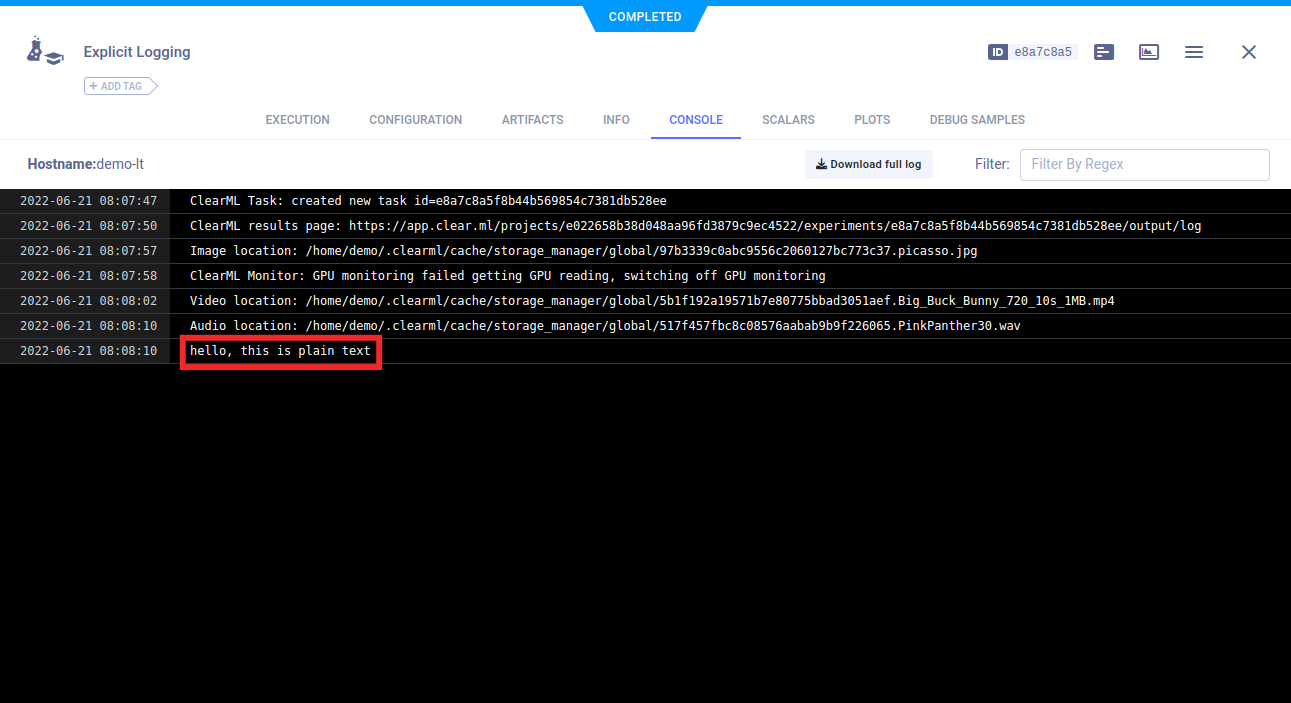
Text
Report text messages by calling Logger.report_text().
logger.report_text("hello, this is plain text")