7.3 KiB
| hide_table_of_contents |
|---|
| true |
0.1.7
Not yet released.
🚀 New features
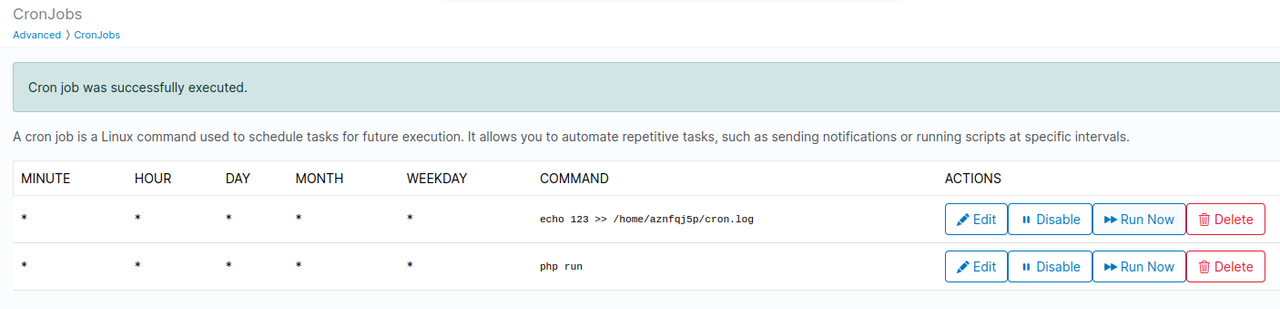
- Cronjobs can now be enabled/disabled and run on demand
- Containerized services
- Ubuntu 24.04 images
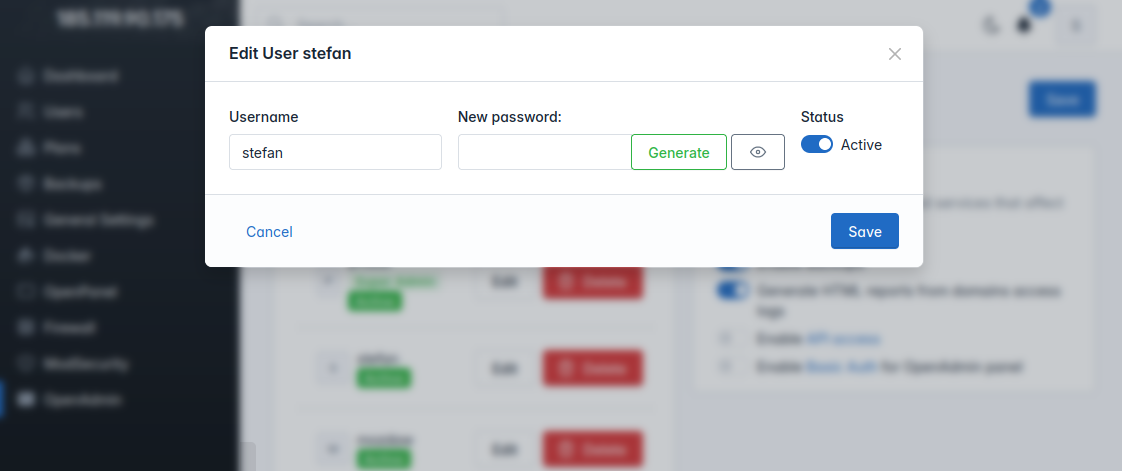
- Admin users can now be edited: rename, change password, suspend/unsuspend from OpenAdmin interface
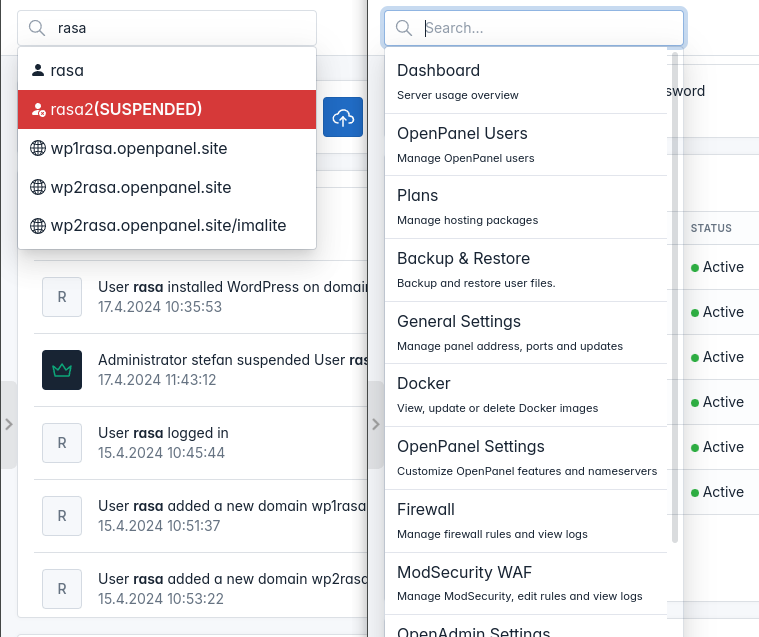
- OpenAdmin search for users, websites and options
- Forbidden usernames list
🐛 Bug fixes
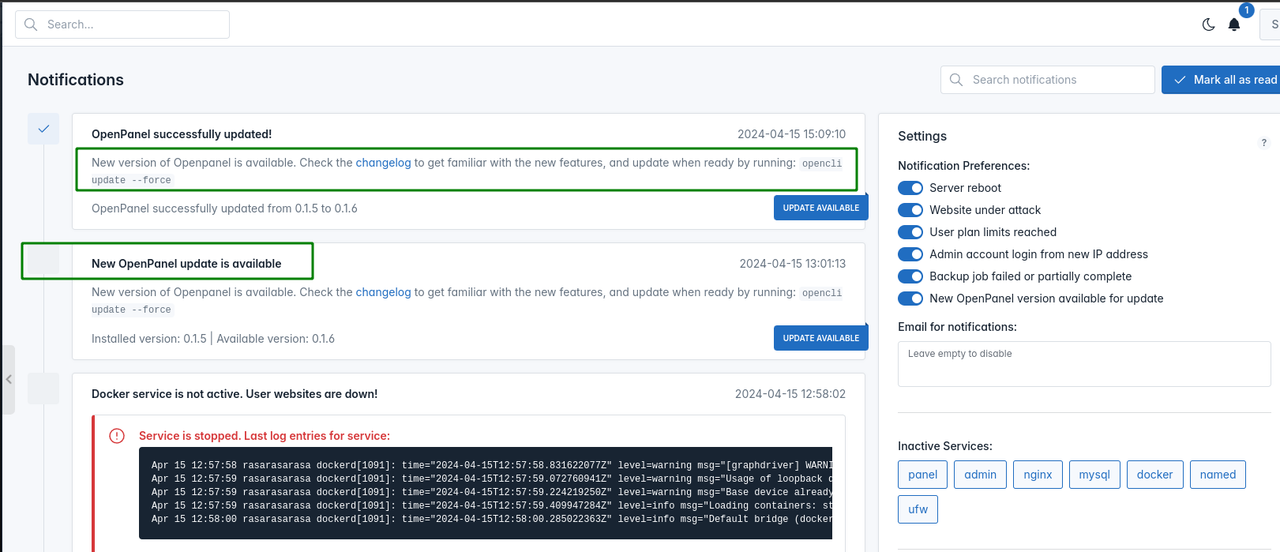
- Fixed bug with successful update message in notification center
- Fixed bug with email alerts not being sent if server does not have a valid ssl
- Fixed js error when there are no docker images on OpenAdmin > Docker Settings
- Fixed bug where the system erroneously flagged initial admin login as a new admin login.
- Fixed bug in the update script where failed updates were being retried.
- Fixed bug with leftover DNS zones from domains removed while the Named service is down
- Fixed multiple bugs with the install script
- Fixed bug with pip install errors on python 3.11
- Fixed bug with Nginx service unable to start if network is down during the installation or if ip.openpanel.co is unreachable.
- Fixed bug with
opencli adminreturning error instead of IPv4 address from external service. - Fixed false-positive error bug when adding user via OpenAdmin interface.
- Fixed bug with search input on OpenAdmin > Firewall page.
💅 Polish
- SSH service status is now restored after reboot
- Generate password button on OpenAdmin > Users now toggles the password field visible.
- Sidebar toggle images are now hosted locally.
- Google Cloud Storage is now used as a mirror for installation files.
- All docker images are now hosted on hub.docker.com
- All services in our official docker images are now disabled by default
Improved install
gitis now removed from the install script- Added checks for failed wget (reported by germangc125)
Cron disable
Users can now pause/unpause cronjobs and execute them out of schedule.
When troubleshooting cronjob, you can add >> /home/USERNAME/CRON.log 2>&1 in the cron command and output will be stored in the file everytime the cron is executed.
Edit Admin Users
Admin users can now be edited: rename, change password, suspend/unsuspend from OpenAdmin interface.
Note: Super admin role can not be suspended or deleted.
Admin search
OpenAdmin has been enhanced with a search feature, enabling Administrators to swiftly navigate the OpenAdmin interface and locate various items. This search functionality covers:
- Users
- Websites
- OpenAdmin pages
Success message
Fixed bug with success message "OpenPanel successfully updated!" not dismissing the "New OpenPanel update is available" message.
Fixed bug with wrong description added for successfull update.
Skip version
Administrators now have the ability to specify which OpenPanel versions to skip during updates by modifying the /etc/openpanel/upgrade/skip_versions file.
This feature proves handy when manually updating from an older version and wishing to skip certain intermediate versions.
For instance, if a user is updating from OpenPanel 0.1.3 with autopatches disabled, the update process would typically progress from 0.1.4 to 0.1.5, then to 0.1.6, and finally to the latest version, 0.1.7.
However, if there are minimal differences between versions 0.1.4 and 0.1.5, an admin can opt to skip version 0.1.4 by appending it to the /etc/openpanel/upgrade/skip_versions file:
echo 0.1.4 >> /etc/openpanel/upgrade/skip_versions
Consequently, during the update procedure, specified version 0.1.4 will be skipped.
It's worth noting that while skipping versions is possible, it's generally not recommended since each update typically takes around 30 seconds.
In the event of a failed update to a particular version, the opencli update scripts will automatically add that version to the /etc/openpanel/upgrade/skip_versions file to prevent future attempts at updating to it.
Forbidden Username
Both opencli user-add and opencli user-rename scripts now use an external list of forbidden names from: /usr/local/admin/scripts/helpers/forbidden_usernames.txt file. Administrators can add usernames to this list.
test
restart
reboot
shutdown
exec
root
admin
ftp
lsws
litespeed
1000
vsftpd
apache2
apache
nginx
php
mysql
mysqld
www-data
openpanel
SSH after reboot
SSH service inside users docker containers is disabled by default when account is created, and in OpenPanel < 0.1.6 was also disabled by defualt when server is rebooted.
We now store the ssh service status for each user and if enabled, after reboot will be re-enabled. note: ssh service for users uses a random port, so after reboot the port is changed.
hub.docker.com
OpenPanel official docker images are now hosted on hub.docker.com
- Nginx stack: https://hub.docker.com/r/openpanel/nginx/tags
- Apache stack: https://hub.docker.com/r/openpanel/apache/tags
Disabled services
In order to reduce the memory footprint of Docker containers, we are implementing breaking changes to our official Docker images for Nginx and Apache:
- NodeJS, Python, PM2, and WP-CLI are removed from the images. They are installed only when needed: when a user adds a WordPress website or a Node.js/Python application.
- All services are disabled by default and will only be enabled when needed. MySQL is enabled when adding the first database or user, webservers are started only when a domain is added, SSH only when SSH access is enabled, cron service after cronjob is added, etc.
This ensures that only the services that are actually used are running.
With these changes, we managed to lower idle CPU & Memory Usage of new user accounts from 680MB to less than 10MB.
Ubuntu24 images
Both official images openpanel/nginx and openpanel/apache now use Ubuntu 24.04 as the base images. This change fixes 16 vulnerabilities in the previous Ubuntu 22.04 docker image.
Containerized services
MySQL service is now run inside a docker container. This allows Admins to set cpu and memory limits for the service, as well to easily manage backup and restore.
Example, restart mysql container:
docker restart openpanel_mysql
Example, backup mysql data locally:
docker run --rm \
--mount source=openpanel_mysql_data,target=<target> \
-v $(pwd):/backup \
busybox \
tar -czvf /backup/<backup-filename>.tar.gz <target>
Example, backup mysql data to AWS:
docker run --rm \
-v openpanel_mysql_data:/var/lib/mysql \
--env AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID="<xxx>" \
--env AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY="<xxx>" \
--env AWS_S3_BUCKET_NAME="<xxx>" \
--entrypoint backup \
offen/docker-volume-backup:v2