mirror of
https://github.com/clearml/clearml-server
synced 2025-02-07 13:33:42 +00:00
253 lines
11 KiB
Markdown
253 lines
11 KiB
Markdown
# TRAINS Server
|
|
|
|
## Auto-Magical Experiment Manager & Version Control for AI
|
|
|
|
[](https://img.shields.io/badge/license-SSPL-green.svg)
|
|
[](https://img.shields.io/badge/python-3.6%20%7C%203.7-blue.svg)
|
|
[](https://img.shields.io/github/release-pre/allegroai/trains-server.svg)
|
|
[](https://img.shields.io/badge/status-beta-yellow.svg)
|
|
|
|
## Introduction
|
|
|
|
The **trains-server** is the backend service infrastructure for [TRAINS](https://github.com/allegroai/trains).
|
|
It allows multiple users to collaborate and manage their experiments.
|
|
By default, TRAINS is set up to work with the TRAINS demo server, which is open to anyone and resets periodically.
|
|
In order to host your own server, you will need to install **trains-server** and point TRAINS to it.
|
|
|
|
**trains-server** contains the following components:
|
|
|
|
* The TRAINS Web-App, a single-page UI for experiment management and browsing
|
|
* RESTful API for:
|
|
* Documenting and logging experiment information, statistics and results
|
|
* Querying experiments history, logs and results
|
|
* Locally-hosted file server for storing images and models making them easily accessible using the Web-App
|
|
|
|
You can quickly setup your **trains-server** using a pre-built Docker image (see [Installation](#installation)).
|
|
|
|
When new releases are available, you can upgrade your pre-built Docker image (see [Upgrade](#upgrade)).
|
|
|
|
The **trains-server's** code is freely available [here](https://github.com/allegroai/trains-server).
|
|
|
|
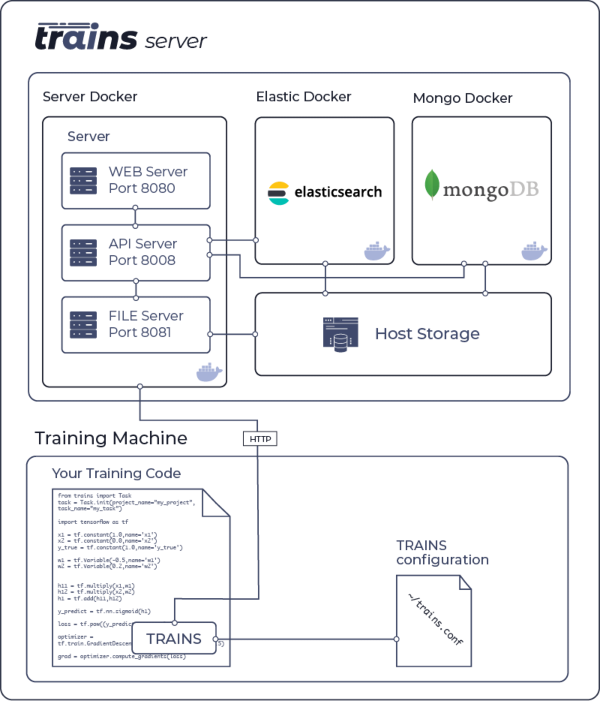
## System diagram
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
## Installation - AWS
|
|
|
|
Use our pre-installed Amazon Machine Image for easy deployment in AWS.
|
|
|
|
Details and instructions can be found [here](docs/install_aws.md).
|
|
|
|
## Installation - Docker
|
|
|
|
This section contains the instructions to setup and launch a pre-built Docker image for the **trains-server**.
|
|
This is the quickest way to get started with your own server.
|
|
Alternatively, you can build the entire trains-server architecture using the code available in our repositories.
|
|
|
|
**Please Note**:
|
|
* This Docker image was tested with Linux, only. For Windows users, we recommend running the server
|
|
on a Linux virtual machine.
|
|
|
|
* All command-line instructions below assume you're using `bash`.
|
|
|
|
### Prerequisites
|
|
|
|
Make sure you are logged in as a user with sudo privileges.
|
|
|
|
### Setup
|
|
|
|
#### Step 1: Install Docker CE
|
|
|
|
In order to run the pre-packaged **trains-server**, install Docker.
|
|
|
|
* See [Supported platforms](https://docs.docker.com/install//#support) in the Docker documentation for instructions
|
|
|
|
* For example, to install in [Ubuntu](https://docs.docker.com/install/linux/docker-ce/ubuntu/) / Mint (x86_64/amd64):
|
|
|
|
```bash
|
|
sudo apt-get install -y apt-transport-https ca-certificates curl software-properties-common
|
|
curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo apt-key add -
|
|
. /etc/os-release
|
|
sudo add-apt-repository "deb [arch=amd64] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu $UBUNTU_CODENAME stable"
|
|
sudo apt-get update
|
|
sudo apt-get install -y docker-ce
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
#### Step 2: Setup the Docker daemon
|
|
|
|
To run the ElasticSearch Docker container, setup the Docker daemon by modifying the default
|
|
values required by Elastic in your Docker configuration file (see [Notes for production use and defaults](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/master/docker.html#_notes_for_production_use_and_defaults)). We provide instructions for the most common Docker configuration files.
|
|
|
|
Edit or create the Docker configuration file:
|
|
|
|
* If your system contains a `/etc/sysconfig/docker` Docker configuration file, edit it.
|
|
|
|
Add the options in quotes to the available arguments in the `OPTIONS` section:
|
|
|
|
```bash
|
|
OPTIONS="--default-ulimit nofile=1024:65536 --default-ulimit memlock=-1:-1"
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
* Otherwise, edit `/etc/docker/daemon.json` (if it exists) or create it (if it does not exist).
|
|
|
|
Add or modify the `defaults-ulimits` section as shown below. Be sure the `defaults-ulimits` section contains the `nofile` and `memlock` sub-sections and values shown.
|
|
|
|
**Note**: Your configuration file may contain other sections. If so, confirm that the sections are separated by commas (valid JSON format). For more information about Docker configuration files, see [Daemon configuration file](https://docs.docker.com/engine/reference/commandline/dockerd/#daemon-configuration-file) in the Docker documentation.
|
|
|
|
The **trains-server** required defaults values are:
|
|
|
|
```json
|
|
{
|
|
"default-ulimits": {
|
|
"nofile": {
|
|
"name": "nofile",
|
|
"hard": 65536,
|
|
"soft": 1024
|
|
},
|
|
"memlock":
|
|
{
|
|
"name": "memlock",
|
|
"soft": -1,
|
|
"hard": -1
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
#### Step 3: Restart the Docker daemon
|
|
|
|
After modifying the configuration file, restart the Docker daemon:
|
|
|
|
```bash
|
|
sudo service docker stop
|
|
sudo service docker start
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
#### Step 4: Set the Maximum Number of Memory Map Areas
|
|
|
|
The maximum number of memory map areas a process can use is defined
|
|
using the `vm.max_map_count` kernel setting.
|
|
|
|
Elastic requires that `vm.max_map_count` is at least 262144 (see [Production mode](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/master/docker.html#docker-cli-run-prod-mode)).
|
|
|
|
* For CentOS 7, Ubuntu 16.04, Mint 18.3, Ubuntu 18.04 and Mint 19 users, we tested the following commands to set
|
|
`vm.max_map_count`:
|
|
|
|
```bash
|
|
sudo echo "vm.max_map_count=262144" > /tmp/99-trains.conf
|
|
sudo mv /tmp/99-trains.conf /etc/sysctl.d/99-trains.conf
|
|
sudo sysctl -w vm.max_map_count=262144
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
* For information about setting this parameter on other systems, see the [elastic](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/docker.html#docker-cli-run-prod-mode) documentation.
|
|
|
|
#### Step 5: Choose a Data Directory
|
|
|
|
Choose a directory on your system in which all data maintained by the **trains-server** is stored.
|
|
Create this directory, and set its owner and group to `uid` 1000. The data stored in this directory will include the database, uploaded files and logs.
|
|
|
|
For example, if your data directory is `/opt/trains`, then use the following command:
|
|
|
|
```bash
|
|
sudo mkdir -p /opt/trains/data/elastic && sudo chown -R 1000:1000 /opt/trains
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
### Launching Docker Containers
|
|
|
|
Launch the Docker containers. For example, if your data directory is `/opt/trains`,
|
|
then use the following commands:
|
|
|
|
```bash
|
|
sudo docker run -d --restart="always" --name="trains-elastic" -e "ES_JAVA_OPTS=-Xms2g -Xmx2g" -e "bootstrap.memory_lock=true" -e "cluster.name=trains" -e "discovery.zen.minimum_master_nodes=1" -e "node.name=trains" -e "script.inline=true" -e "script.update=true" -e "thread_pool.bulk.queue_size=2000" -e "thread_pool.search.queue_size=10000" -e "xpack.security.enabled=false" -e "xpack.monitoring.enabled=false" -e "cluster.routing.allocation.node_initial_primaries_recoveries=500" -e "node.ingest=true" -e "http.compression_level=7" -e "reindex.remote.whitelist=*.*" -e "script.painless.regex.enabled=true" --network="host" -v /opt/trains/data/elastic:/usr/share/elasticsearch/data docker.elastic.co/elasticsearch/elasticsearch:5.6.16
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
```bash
|
|
sudo docker run -d --restart="always" --name="trains-mongo" -v /opt/trains/data/mongo/db:/data/db -v /opt/trains/data/mongo/configdb:/data/configdb --network="host" mongo:3.6.5
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
```bash
|
|
sudo docker run -d --restart="always" --name="trains-fileserver" --network="host" -v /opt/trains/logs:/var/log/trains -v /opt/trains/data/fileserver:/mnt/fileserver allegroai/trains:latest fileserver
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
```bash
|
|
sudo docker run -d --restart="always" --name="trains-apiserver" --network="host" -v /opt/trains/logs:/var/log/trains allegroai/trains:latest apiserver
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
```bash
|
|
sudo docker run -d --restart="always" --name="trains-webserver" --network="host" -v /opt/trains/logs:/var/log/trains allegroai/trains:latest webserver
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
After the **trains-server** Dockers are up, the following are available:
|
|
|
|
* API server on port `8008`
|
|
* Web server on port `8080`
|
|
* File server on port `8081`
|
|
|
|
### Configuring **trains**
|
|
|
|
Once you have installed the **trains-server**, make sure to configure **trains** to use your locally installed server (and not the demo server).
|
|
|
|
If you have already installed **trains**, run the `trains-init` command for an interactive setup or edit your `trains.conf` file and make sure the `api.host` value is configured as follows:
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
api {
|
|
host: "http://localhost:8008"
|
|
}
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
See [Installing and Configuring TRAINS](https://github.com/allegroai/trains#installing-and-configuring-trains) for more details.
|
|
|
|
## What next?
|
|
|
|
Now that the **trains-server** is installed, and TRAINS is configured to use it,
|
|
you can [use](https://github.com/allegroai/trains#using-trains) TRAINS in your experiments and view them in the web server,
|
|
for example http://localhost:8080
|
|
|
|
## Upgrade
|
|
|
|
We are constantly updating, improving and adding to the **trains-server**.
|
|
New releases will include new pre-built Docker images.
|
|
When we release a new version and include a new pre-built Docker image for it, upgrade as follows:
|
|
|
|
1. Shut down and remove each of your Docker instances using the following commands:
|
|
|
|
sudo docker stop <docker-name>
|
|
sudo docker rm -v <docker-name>
|
|
|
|
The Docker names are (see [Launching Docker Containers](#launching-docker-containers)):
|
|
|
|
* `trains-elastic`
|
|
* `trains-mongo`
|
|
* `trains-fileserver`
|
|
* `trains-apiserver`
|
|
* `trains-webserver`
|
|
|
|
2. We highly recommend backing up your data directory!. A simple way to do that is using `tar`:
|
|
|
|
For example, if your data directory is `/opt/trains`, use the following command:
|
|
|
|
sudo tar czvf ~/trains_backup.tgz /opt/trains/data
|
|
|
|
This back ups all data to an archive in your home directory.
|
|
|
|
To restore this example backup, use the following command:
|
|
|
|
sudo rm -R /opt/trains/data
|
|
sudo tar -xzf ~/trains_backup.tgz -C /opt/trains/data
|
|
|
|
3. Launch the newly released Docker image (see [Launching Docker Containers](#launching-docker-containers)).
|
|
|
|
## License
|
|
|
|
[Server Side Public License v1.0](https://github.com/mongodb/mongo/blob/master/LICENSE-Community.txt)
|
|
|
|
**trains-server** relies on both [MongoDB](https://github.com/mongodb/mongo) and [ElasticSearch](https://github.com/elastic/elasticsearch).
|
|
With the recent changes in both MongoDB's and ElasticSearch's OSS license, we feel it is our responsibility as a
|
|
member of the community to support the projects we love and cherish.
|
|
We believe the cause for the license change in both cases is more than just,
|
|
and chose [SSPL](https://www.mongodb.com/licensing/server-side-public-license) because it is the more general and flexible of the two licenses.
|
|
|
|
This is our way to say - we support you guys!
|