5.6 KiB
| title |
|---|
| Pipeline from Decorators |
The pipeline_from_decorator.py
example demonstrates the creation of a pipeline in ClearML using the PipelineDecorator
class.
This example creates a pipeline incorporating four tasks, each of which is created from a python function using a custom decorator:
executing_pipeline- Implements the pipeline controller which defines the pipeline structure and execution logic.step_one- Downloads and processes data.step_two- Further processes the data fromstep_one.step_three- Uses the processed data fromstep_twoto train a model.
The pipeline steps, defined in the step_one, step_two, and step_three functions, are each wrapped with the
@PipelineDecorator.component
decorator, which creates a ClearML pipeline step for each one when the pipeline is executed.
The logic that executes these steps and controls the interaction between them is implemented in the executing_pipeline
function. This function is wrapped with the @PipelineDecorator.pipeline
decorator which creates the ClearML pipeline task when it is executed.
The sections below describe in more detail what happens in the pipeline controller and steps.
Pipeline Controller
In this example, the pipeline controller is implemented by the executing_pipeline function.
Using the @PipelineDecorator.pipeline decorator creates a ClearML Controller Task from the function when it is executed.
For detailed information, see @PipelineDecorator.pipeline.
In the example script, the controller defines the interactions between the pipeline steps in the following way:
- The controller function passes its argument,
pickle_url, to the pipeline's first step (step_one) - The returned data from the first step,
data_frame, is passed tostep_two - The second step's output,
preprocessed_data, is modified within the pipeline execution logic - The modified data is passed to the third step,
step_three.
Pipeline Steps
Using the @PipelineDecorator.component decorator will make the function a pipeline component that can be called from the
pipeline controller, which implements the pipeline's execution logic. For detailed information, see @PipelineDecorator.component.
When the pipeline controller calls a pipeline step, a corresponding ClearML task will be created. For this reason, each function which makes up a pipeline step needs to be self-contained. Notice that all package imports inside the function will be automatically logged as required packages for the pipeline execution step.
Pipeline Execution
PipelineDecorator.set_default_execution_queue('default')
# PipelineDecorator.debug_pipeline()
executing_pipeline(
pickle_url='https://github.com/allegroai/events/raw/master/odsc20-east/generic/iris_dataset.pkl',
)
By default, the pipeline controller and the pipeline steps are launched through ClearML queues.
Use the PipelineDecorator.set_default_execution_queue
method to specify the execution queue of all pipeline steps. The execution_queue parameter of the PipelineDecorator.component
decorator overrides the default queue value for the specific step for which it was specified.
:::note Execution Modes ClearML provides different pipeline execution modes to accommodate development and production use cases. For additional details, see Execution Modes. :::
To run the pipeline, call the pipeline controller function.
WebApp
Pipeline Controller
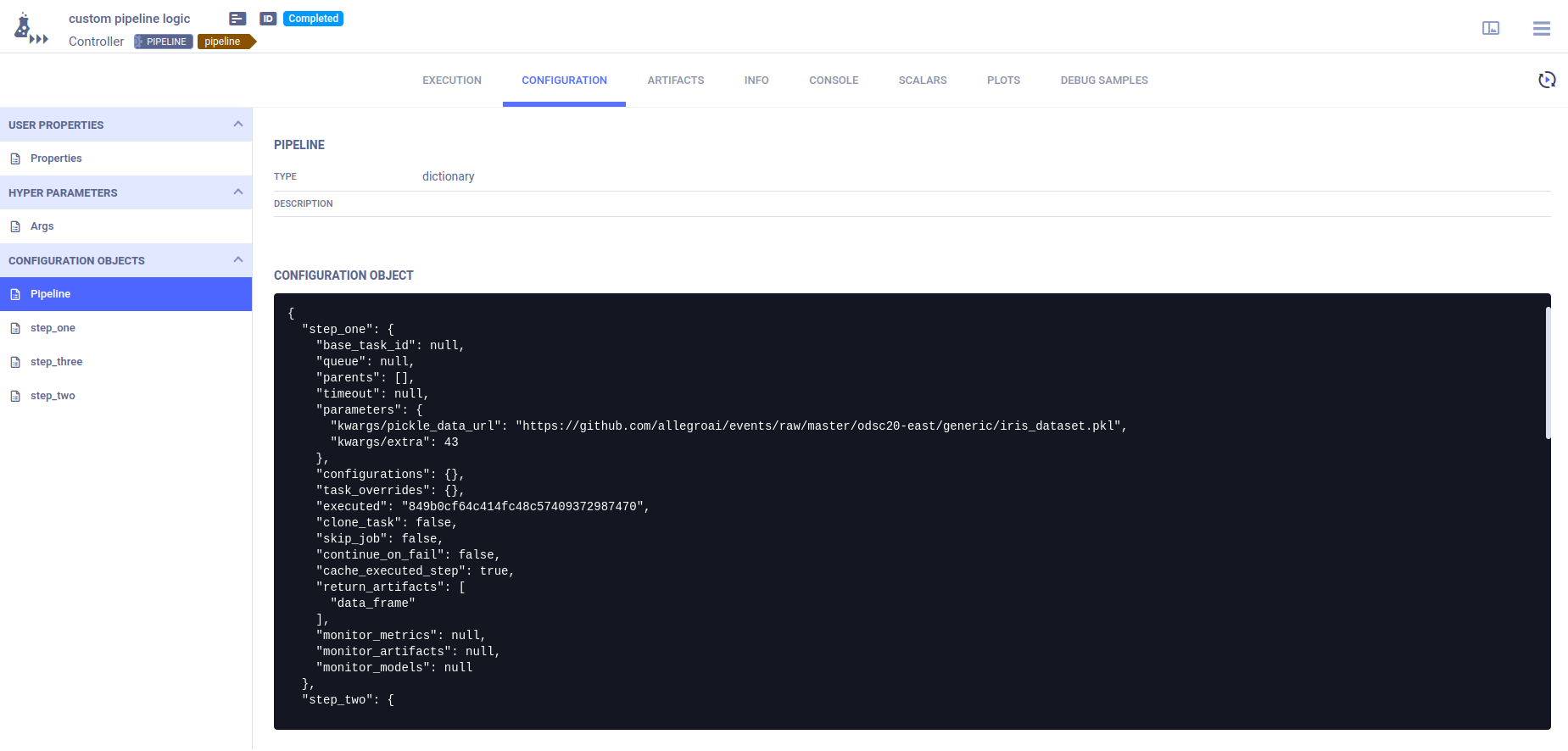
The pipeline controller’s CONFIGURATION page contains the pipeline structure and step definitions in its Configuration Objects section.
The Pipeline configuration object contains the pipeline structure and execution parameters.
An additional configuration object per pipeline step contains the step’s definitions and execution parameters.
The pipeline controller’s RESULTS > PLOTS page provides summary details for the pipeline execution.
The Execution Flow graphically summarizes the pipeline's execution. Hover over each step to view its details.
The Execution Details table provides the pipeline execution details in table format.
Pipeline Steps
Each function step’s arguments are stored in their respective task’s CONFIGURATION > HYPER PARAMETERS > kwargs.
Values that were listed in the return_valuesparameter of the PipelineDecorator.component decorator are stored as
artifacts in the relevant step's task. These artifacts can be viewed in the step task’s ARTIFACTS tab.