5.5 KiB
| title |
|---|
| Pipeline from Functions |
The pipeline_from_functions.py example script demonstrates the creation of a pipeline using the PipelineController class.
This example creates a pipeline incorporating four tasks, three of which are created from a function:
step_one- Downloads and processes data.step_two- Further processes the data fromstep_one.step_three- Uses the processed data fromstep_twoto train a model.
The fourth task is the pipeline task, which is created when the pipeline is launched.
The step functions will be registered as pipeline steps when they are added to the pipeline controller.
When the pipeline steps are executed, corresponding ClearML Tasks are created. For this reason, each function which makes up a pipeline step needs to be self-contained. Notice that all package imports inside the function will be automatically logged as required packages for the pipeline execution step.
Pipeline Controller
-
Create the PipelineController object.
pipe = PipelineController( name='pipeline demo', project='examples', version='0.0.1', add_pipeline_tags=False, ) -
Set the default execution queue to be used. All the pipeline steps will be enqueued for execution in this queue (unless overridden by the
execution_queueparameter of theadd_function_stepmethod).
pipe.set_default_execution_queue('default')
-
Add a pipeline level parameter that can be referenced from any step in the pipeline (see
step_onebelow).pipe.add_parameter( name='url', description='url to pickle file', default='https://github.com/allegroai/events/raw/master/odsc20-east/generic/iris_dataset.pkl' ) -
Build the pipeline (see
PipelineController.add_function_stepfor complete reference).The first step in the pipeline uses the
step_onefunction and uses as its input the pipeline level argument defined above. Its return object will be stored as an artifact under the namedata_frame.pipe.add_function_step( name='step_one', function=step_one, function_kwargs=dict(pickle_data_url='${pipeline.url}'), function_return=['data_frame'], cache_executed_step=True, )The second step in the pipeline uses the
step_twofunction and uses as its input the first step’s output.This reference implicitly defines the pipeline structure, makingstep_onethe parent step ofstep_two.Its return object will be stored as an artifact under the name
processed_data.pipe.add_function_step( name='step_two', # parents=['step_one'], # the pipeline will automatically detect the dependencies based on the kwargs inputs function=step_two, function_kwargs=dict(data_frame='${step_one.data_frame}'), function_return=['processed_data'], cache_executed_step=True, )The third step in the pipeline uses the
step_threefunction and uses as its input the second step’s output. This reference implicitly defines the pipeline structure, makingstep_twothe parent step ofstep_three.Its return object will be stored as an artifact under the name
model:pipe.add_function_step( name='step_three', # parents=['step_two'], # the pipeline will automatically detect the dependencies based on the kwargs inputs function=step_three, function_kwargs=dict(data='${step_two.processed_data}'), function_return=['model'], cache_executed_step=True, ) -
Run the pipeline.
pipe.start()The pipeline will be launched remotely, through the
servicesqueue, unless otherwise specified.
WebApp
When the experiment is executed, the terminal returns the task ID, and links to the pipeline controller task page and pipeline page.
ClearML Task: created new task id=bc93610688f242ecbbe70f413ff2cf5f
ClearML results page: https://app.clear.ml/projects/462f48dba7b441ffb34bddb783711da7/experiments/bc93610688f242ecbbe70f413ff2cf5f/output/log
ClearML pipeline page: https://app.clear.ml/pipelines/462f48dba7b441ffb34bddb783711da7/experiments/bc93610688f242ecbbe70f413ff2cf5f
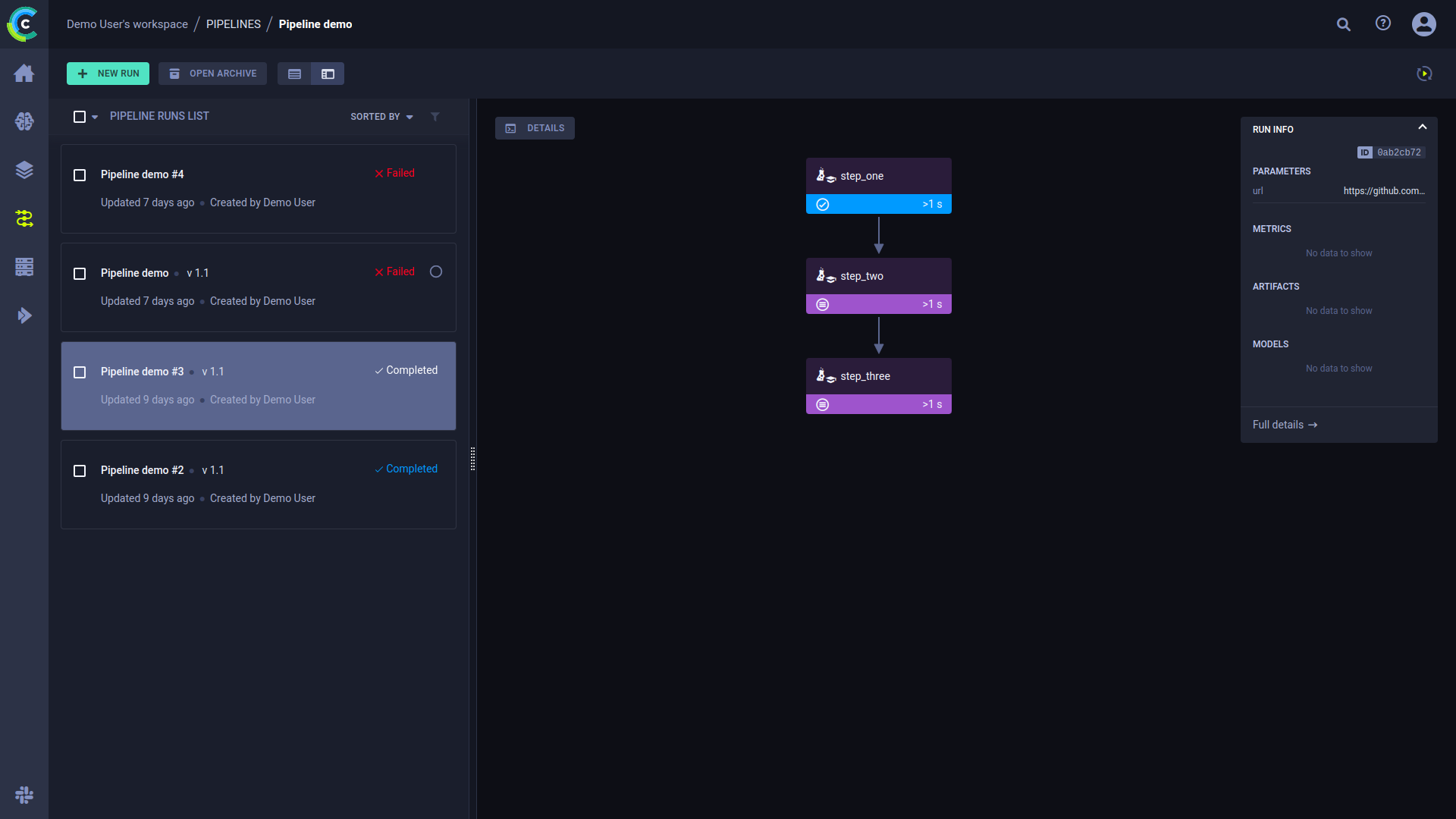
The pipeline run’s page contains the pipeline’s structure, the execution status of every step, as well as the run’s configuration parameters and output.
To view a run’s complete information, click Full details on the bottom of the Run Info panel, which will open the pipeline’s controller task page.
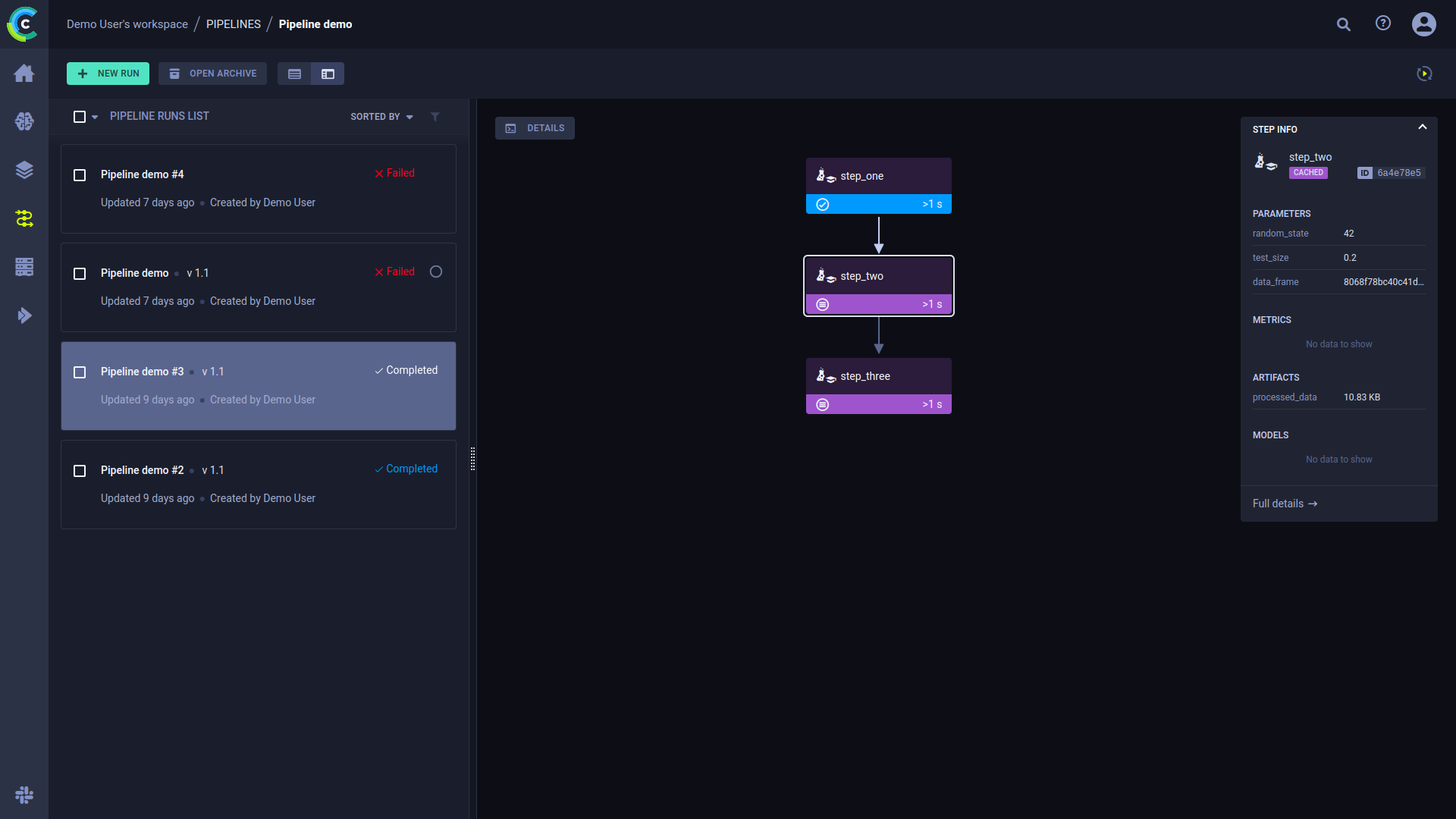
Click a step to see an overview of its details.
Console and Code
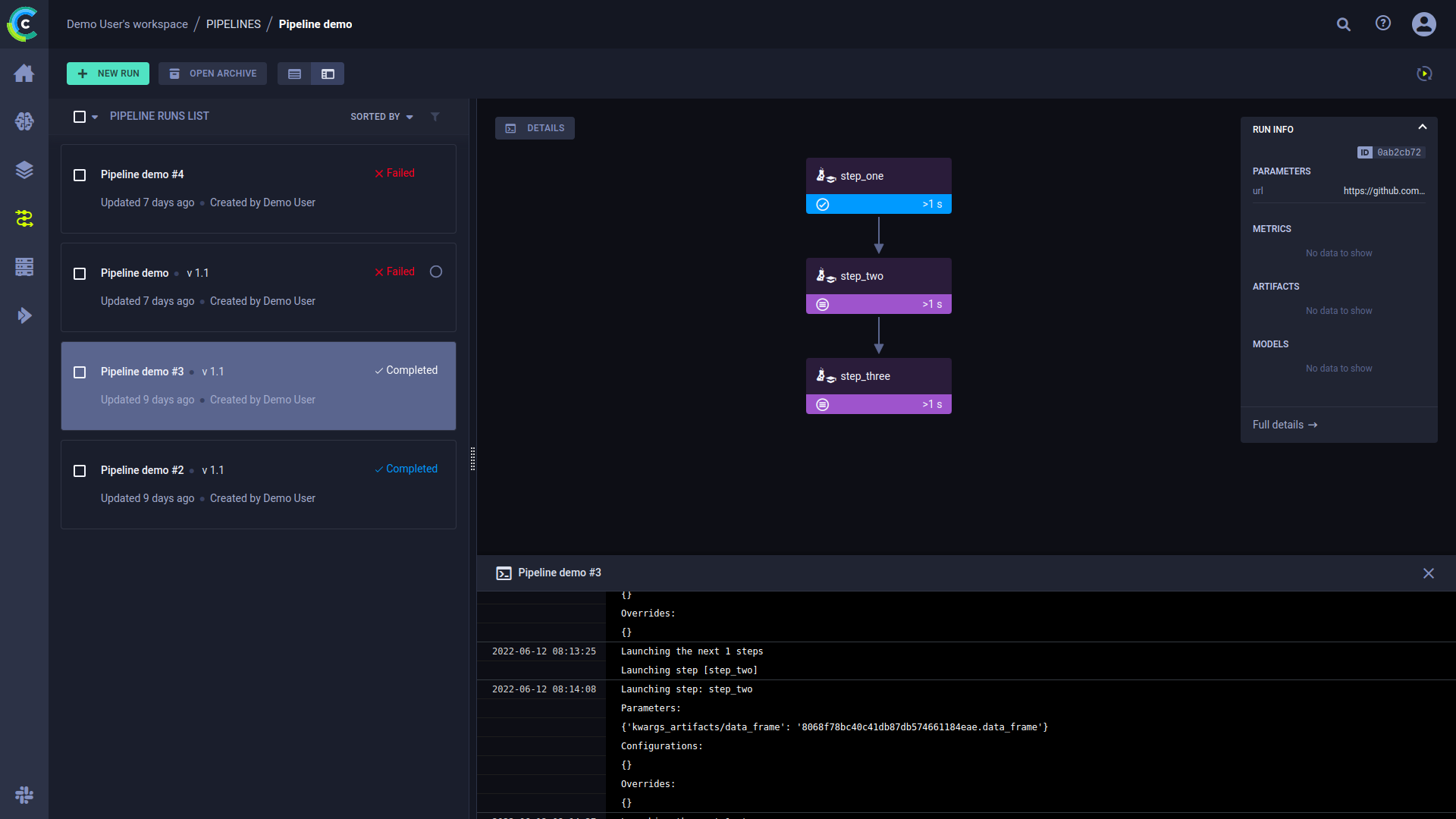
Click DETAILS to view a log of the pipeline controller’s console output.
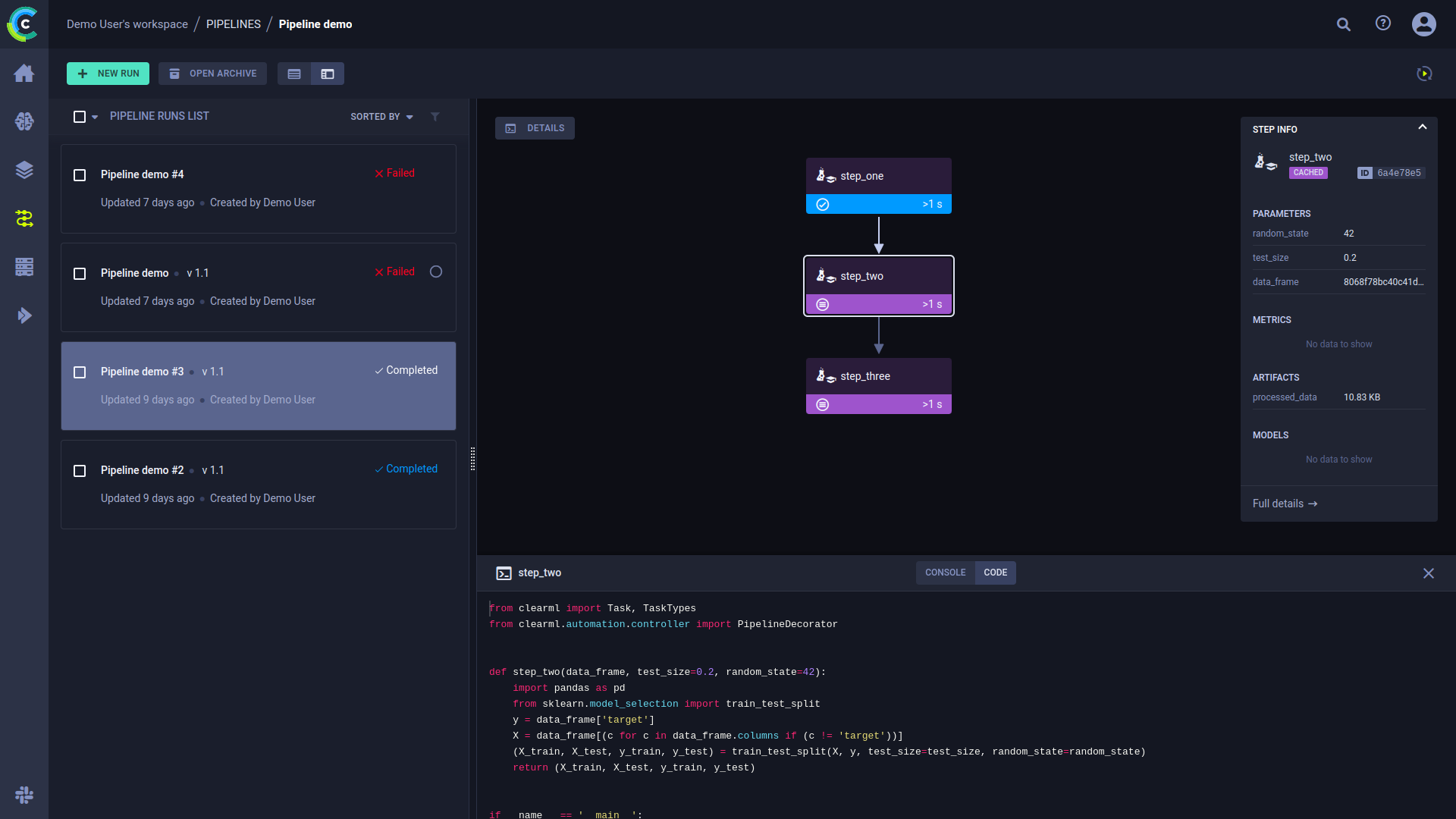
Click on a step to view its console output. You can also view the selected step’s code by clicking CODE on top of the console log.