5.5 KiB
| title |
|---|
| Pipeline from Functions |
The pipeline_from_functions.py example script demonstrates the creation of a pipeline using the PipelineController class.
This example creates a pipeline incorporating four tasks, three of which are created from a function:
step_one- Downloads and processes data.step_two- Further processes the data fromstep_one.step_three- Uses the processed data fromstep_twoto train a model.
The fourth task is the pipeline task, which is created when the pipeline is launched.
The step functions will be registered as pipeline steps when they are added to the pipeline controller.
When the pipeline steps are executed, corresponding ClearML Tasks are created. For this reason, each function which makes up a pipeline step needs to be self-contained. Notice that all package imports inside the function will be automatically logged as required packages for the pipeline execution step.
Pipeline Controller
-
Create the PipelineController object.
pipe = PipelineController( name='pipeline demo', project='examples', version='0.0.1', add_pipeline_tags=False, ) -
Set the default execution queue to be used. All the pipeline steps will be enqueued for execution in this queue (unless overridden by the
execution_queueparameter of theadd_function_stepmethod).
pipe.set_default_execution_queue('default')
-
Add a pipeline level parameter that can be referenced from any step in the pipeline (see
step_onebelow).pipe.add_parameter( name='url', description='url to pickle file', default='https://github.com/allegroai/events/raw/master/odsc20-east/generic/iris_dataset.pkl' ) -
Build the pipeline (see
PipelineController.add_function_stepfor complete reference).The first step in the pipeline uses the
step_onefunction and uses as its input the pipeline level argument defined above. Its return object will be stored as an artifact under the namedata_frame.pipe.add_function_step( name='step_one', function=step_one, function_kwargs=dict(pickle_data_url='${pipeline.url}'), function_return=['data_frame'], cache_executed_step=True, )The second step in the pipeline uses the
step_twofunction and uses as its input the first step’s output.This reference implicitly defines the pipeline structure, makingstep_onethe parent step ofstep_two.Its return object will be stored as an artifact under the name
processed_data.pipe.add_function_step( name='step_two', # parents=['step_one'], # the pipeline will automatically detect the dependencies based on the kwargs inputs function=step_two, function_kwargs=dict(data_frame='${step_one.data_frame}'), function_return=['processed_data'], cache_executed_step=True, )The third step in the pipeline uses the
step_threefunction and uses as its input the second step’s output. This reference implicitly defines the pipeline structure, makingstep_twothe parent step ofstep_three.Its return object will be stored as an artifact under the name
model:pipe.add_function_step( name='step_three', # parents=['step_two'], # the pipeline will automatically detect the dependencies based on the kwargs inputs function=step_three, function_kwargs=dict(data='${step_two.processed_data}'), function_return=['model'], cache_executed_step=True, ) -
Run the pipeline.
pipe.start()The pipeline will be launched remotely, through the
servicesqueue, unless otherwise specified.
WebApp
Pipeline Controller
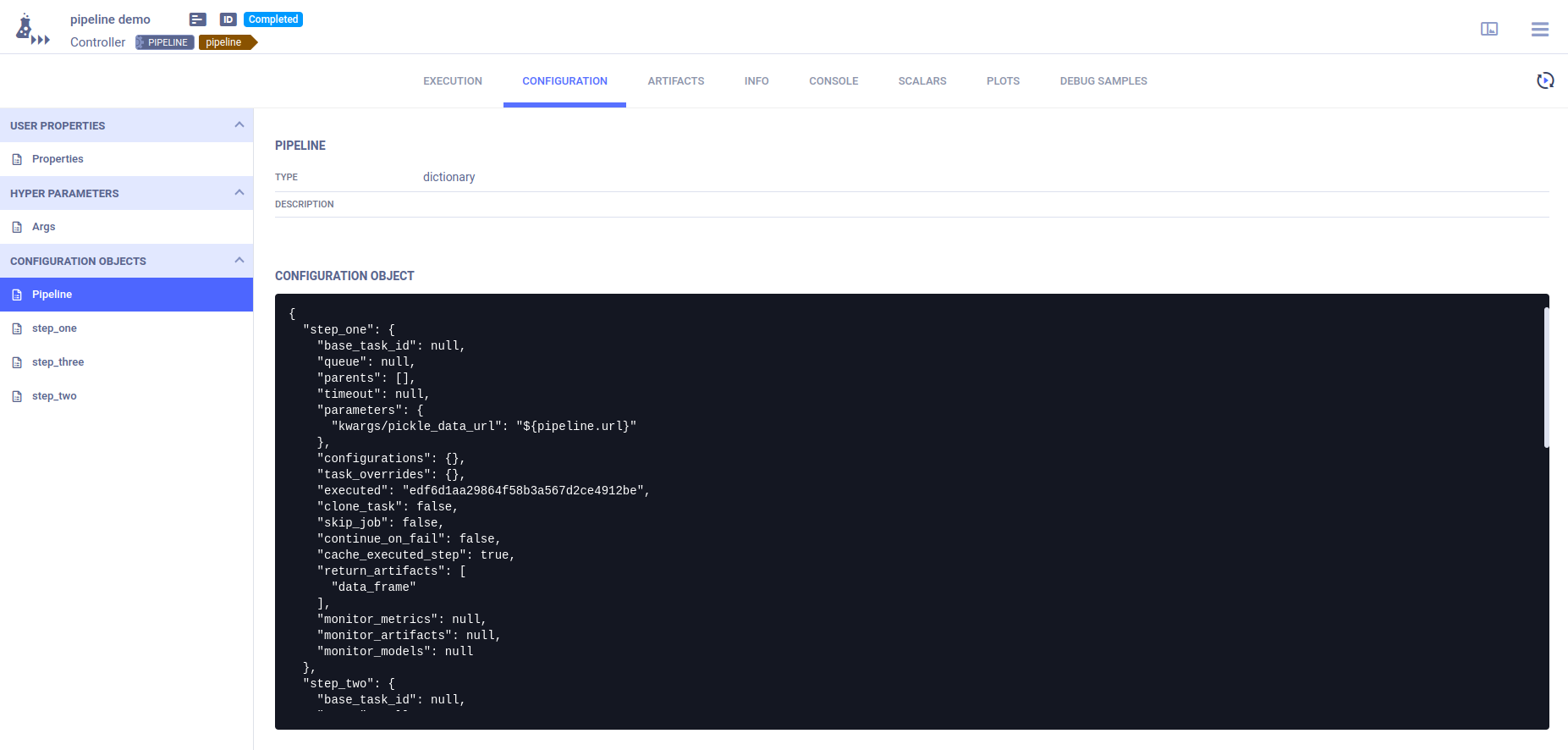
The pipeline controller’s CONFIGURATION page contains the pipeline structure and step definitions in its Configuration Objects section.
The Pipeline configuration object contains the pipeline structure and execution parameters.
An additional configuration object per pipeline step contains the step’s definitions and execution parameters.
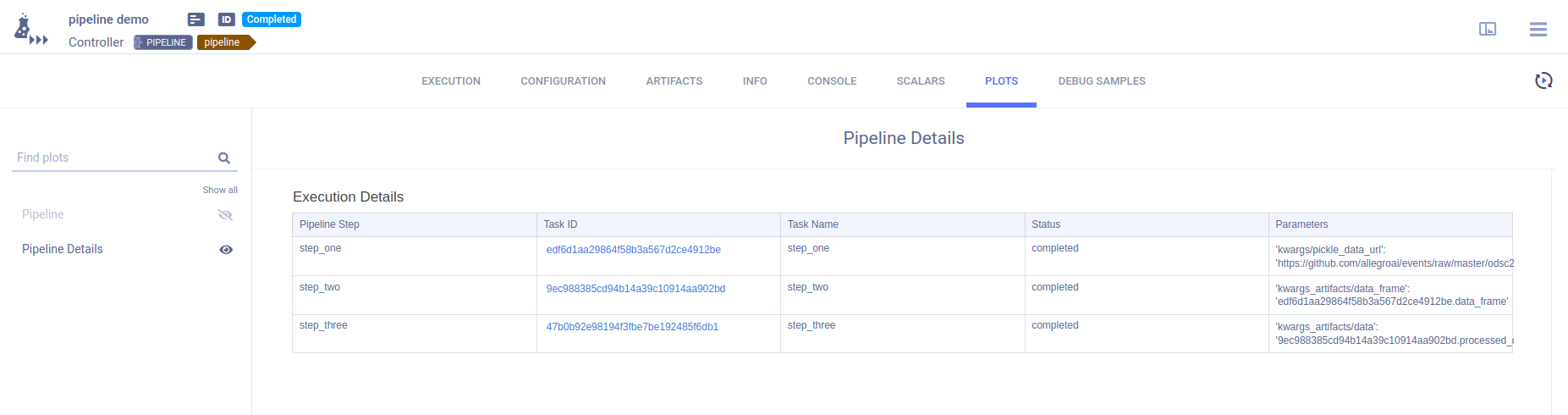
The pipeline controller’s RESULTS > PLOTS page provides summary details for the pipeline execution.
The Execution Flow graphically summarizes the pipeline's execution. Hover over each step to view its details.
The Execution Details table provides the pipeline execution details in table format.
Pipeline Steps
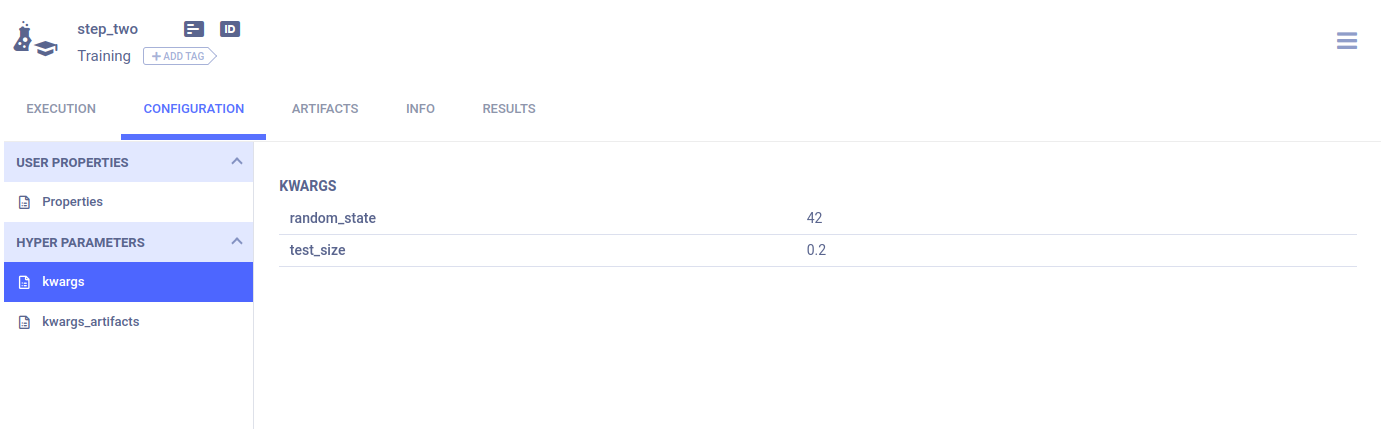
Each function step’s arguments are stored in their respective task’s CONFIGURATION > HYPER PARAMETERS > kwargs.
Values that were listed in the return_valuesparameter of the PipelineDecorator.component decorator are stored as
artifacts in the relevant step's task. These artifacts can be viewed in the step task’s ARTIFACTS tab.