7.6 KiB
| title |
|---|
| Hyperparameter Optimization |
You can automate and boost hyperparameter optimization (HPO) with ClearML's
HyperParameterOptimizer class, which takes care of the entire optimization process
with a simple interface.
ClearML's approach to hyperparameter optimization is scalable, easy to set up and to manage, and it makes it easy to compare results.
Workflow
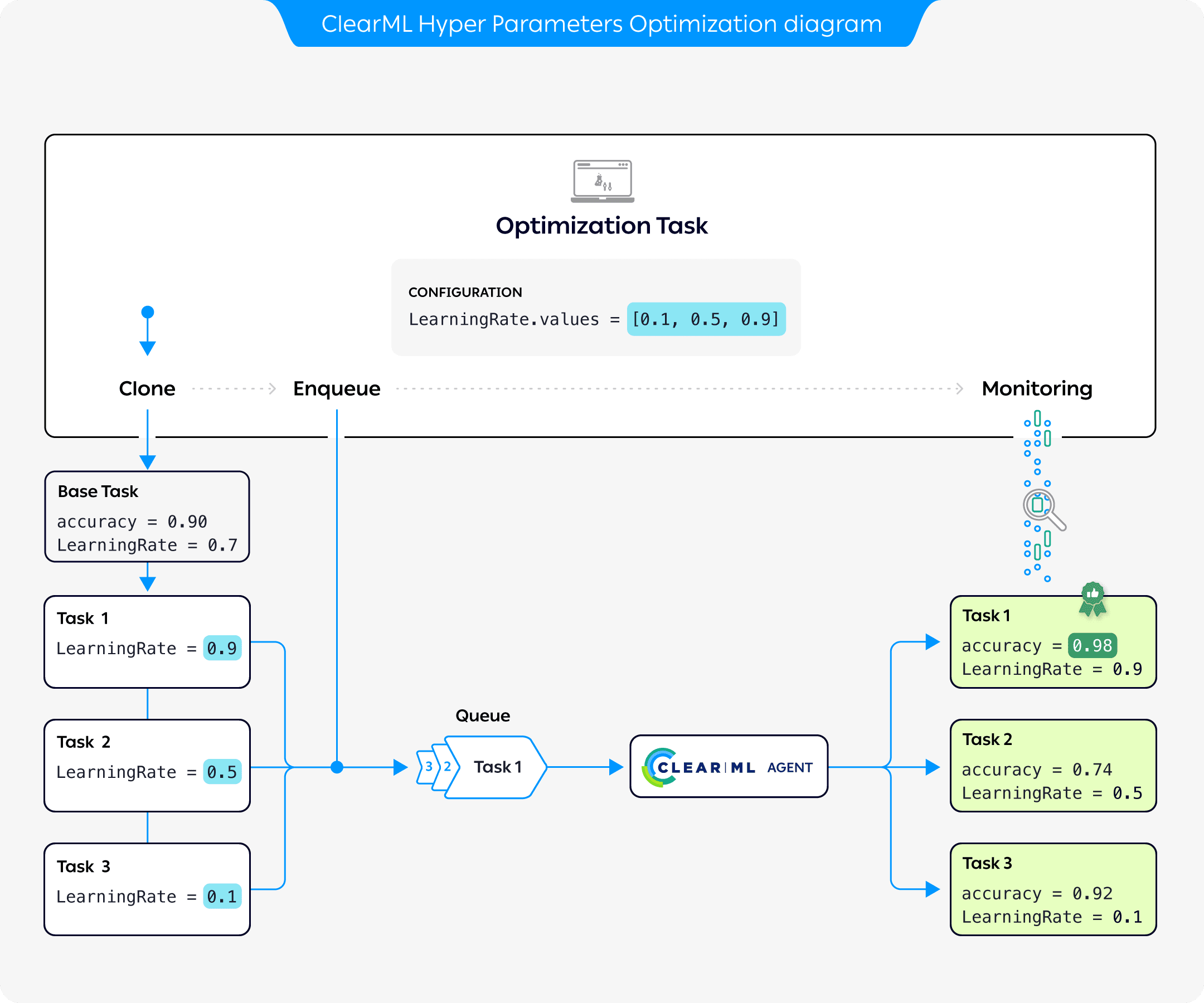
The preceding diagram demonstrates the typical flow of hyperparameter optimization where the parameters of a base task are optimized:
- Configure an Optimization Task with a base task whose parameters will be optimized, optimization targets, and a set of parameter values to test
- Clone the base task. Each clone's parameter is overridden with a value from the optimization task
- Enqueue each clone for execution by a ClearML Agent
- The Optimization Task records and monitors the cloned tasks' configuration and execution details, and returns a summary of the optimization results in tabular and parallel coordinate formats, and in a scalar plot.
Supported Optimizers
The HyperParameterOptimizer class contains ClearML's hyperparameter optimization modules. Its modular design enables
using different optimizers, including existing software frameworks, enabling simple, accurate, and fast hyperparameter
optimization.
- Optuna -
automation.optuna.OptimizerOptuna. Optuna is the default optimizer in ClearML. It makes use of different samplers such as grid search, random, bayesian, and evolutionary algorithms. For more information, see the Optuna documentation. - BOHB -
automation.hpbandster.OptimizerBOHB. BOHB performs robust and efficient hyperparameter optimization at scale by combining the speed of Hyperband searches with the guidance and guarantees of convergence of Bayesian Optimization. For more information about HpBandSter BOHB, see the HpBandSter documentation and a code example. - Random uniform sampling of hyperparameters -
automation.RandomSearch. - Full grid sampling strategy of every hyperparameter combination -
automation.GridSearch. - Custom -
automation.optimization.SearchStrategy- Use a custom class and inherit from the ClearML automation base strategy class.
Defining a Hyperparameter Optimization Search Example
-
Import ClearML's automation modules:
from clearml.automation import UniformParameterRange, UniformIntegerParameterRange from clearml.automation import HyperParameterOptimizer from clearml.automation.optuna import OptimizerOptuna -
Initialize the Task, which will be stored in ClearML Server when the code runs. After the code runs at least once, it can be reproduced, and the parameters can be tuned:
from clearml import Task task = Task.init( project_name='Hyper-Parameter Optimization', task_name='Automatic Hyper-Parameter Optimization', task_type=Task.TaskTypes.optimizer, reuse_last_task_id=False ) -
Define the optimization configuration and resources budget:
optimizer = HyperParameterOptimizer( # specifying the task to be optimized, task must be in system already so it can be cloned base_task_id=TEMPLATE_TASK_ID, # setting the hyperparameters to optimize hyper_parameters=[ UniformIntegerParameterRange('number_of_epochs', min_value=2, max_value=12, step_size=2), UniformIntegerParameterRange('batch_size', min_value=2, max_value=16, step_size=2), UniformParameterRange('dropout', min_value=0, max_value=0.5, step_size=0.05), UniformParameterRange('base_lr', min_value=0.00025, max_value=0.01, step_size=0.00025), ], # setting the objective metric we want to maximize/minimize objective_metric_title='accuracy', objective_metric_series='total', objective_metric_sign='max', # setting optimizer optimizer_class=OptimizerOptuna, # configuring optimization parameters execution_queue='default', max_number_of_concurrent_tasks=2, optimization_time_limit=60., compute_time_limit=120, total_max_jobs=20, min_iteration_per_job=15000, max_iteration_per_job=150000, ):::tip Locating Task ID To locate the base task's ID, go to the task's info panel in the WebApp. The ID appears in the task header. :::
:::tip Multi-objective Optimization If you are using the Optuna framework (see Supported Optimizers), you can list multiple optimization objectives. When doing so, make sure the
objective_metric_title,objective_metric_series, andobjective_metric_signlists are the same length. Each title will be matched to its respective series and sign.For example, the code below sets two objectives: to minimize the
validation/lossmetric and to maximize thevalidation/accuracymetric.objective_metric_title=["validation", "validation"] objective_metric_series=["loss", "accuracy"] objective_metric_sign=["min", "max"]:::
Optimizer Execution Options
The HyperParameterOptimizer provides options to launch the optimization tasks locally or through a ClearML queue.
Start a HyperParameterOptimizer instance using either HyperParameterOptimizer.start()
or HyperParameterOptimizer.start_locally().
Both methods run the optimizer controller locally. start() launches the base task clones through a queue
specified when instantiating the controller, while start_locally() runs the tasks locally.
:::tip Remote Execution
You can also launch the optimizer controller through a queue by using Task.execute_remotely()
before starting the optimizer.
:::
Tutorial
Check out the Hyperparameter Optimization tutorial for a step-by-step guide.
SDK Reference
For detailed information, see the complete HyperParameterOptimizer SDK reference page.