10 KiB
| title |
|---|
| Pipeline from Tasks |
The pipeline_from_tasks.py example demonstrates a simple pipeline, where each step is a ClearML Task.
The pipeline is implemented using the PipelineController class. Steps are added to a PipelineController object, which launches and monitors the steps when executed.
This example incorporates four tasks, each of which is created using a different script:
- Controller Task (pipeline_from_tasks.py) - Implements the pipeline controller, adds the steps (tasks) to the pipeline, and runs the pipeline.
- Step 1 (step1_dataset_artifact.py) - Downloads data and stores the data as an artifact.
- Step 2 (step2_data_processing.py) - Loads the stored data (from Step 1), processes it, and stores the processed data as artifacts.
- Step 3 (step3_train_model.py) - Loads the processed data (from Step 2) and trains a network.
When the controller task is executed, it clones the step tasks, and enqueues the newly cloned tasks for execution. Note that the base tasks from which the steps are cloned are only used as templates and not executed themselves. Also note that for the controller to clone, these base tasks need to exist in the system (as a result of a previous run or using clearml-task).
The controller task itself can be run locally, or, if the controller task has already run at least once and is in the ClearML Server, the controller can be cloned, and the cloned task can be executed remotely.
The sections below describe in more detail what happens in the controller task and in each step task.
The Pipeline Controller
-
Create the pipeline controller object.
pipe = PipelineController( name='pipeline demo', project='examples', version='0.0.1', add_pipeline_tags=False, )name- Name the pipeline controller taskproject- Project where pipeline controller and tasks will be storedversion- Provide a pipeline version. Ifauto_version_bumpis set toTrue, then the version number will be automatically bumped if the same version already exists.add_pipeline_tags- IfTrue, then all pipeline steps are tagged withpipe: <pipeline_task_id>
-
Add Step 1 using the PipelineController.add_step method.
pipe.add_step(name='stage_data', base_task_project='examples', base_task_name='pipeline step 1 dataset artifact')name- The name of Step 1 (stage_data).base_task_projectandbase_task_name- Step 1's base Task to clone (the cloned Task will be executed when the pipeline runs).
-
Add Step 2.
pipe.add_step( name='stage_process', parents=['stage_data', ], base_task_project='examples', base_task_name='pipeline step 2 process dataset', parameter_override={ 'General/dataset_url': '${stage_data.artifacts.dataset.url}', 'General/test_size': 0.25 }, pre_execute_callback=pre_execute_callback_example, post_execute_callback=post_execute_callback_example )In addition to the parameters included in Step 1, input the following:
parents- The names of the steps, which the current step depends upon their completion to begin execution. In this instance, the execution of Step 2 (stage_process) depends upon the completion of Step 1 (stage_data).parameter_override- Pass the URL of the data artifact from Step 1 to Step 2. Override the value of the parameter whose key isdataset_url(in the parameter group namedGeneral). Override it with the URL of the artifact nameddataset. Also override the test size.
:::important Syntax of the parameter_override Value For other examples of
parameter_overridesyntax, see PipelineController.add_step. :::pre_execute_callback- The pipeline controller will execute the input callback function before the pipeline step is executed. If the callback function returnsFalse, the pipeline step will be skipped.post_execute_callback- The pipeline controller will execute the input callback function after the pipeline step is executed.
-
Add Step 3.
pipe.add_step( name='stage_train', parents=['stage_process', ], base_task_project='examples', base_task_name='pipeline step 3 train model', parameter_override={'General/dataset_task_id': '${stage_process.id}'})name- The name of Step 3 (stage_train).parents- The start of Step 3 (stage_train) depends upon the completion of Step 2 (stage_process).parameter_override- Pass the ID of the Step 2 Task to the Step 3 Task. This is the ID of the cloned Task, not the base Task.
-
Run the pipeline.
# Starting the pipeline (in the background) pipe.start()
Step 1 - Downloading the Data
In the Step 1 Task (step1_dataset_artifact.py):
-
Clone base Task and enqueue it for execution using
Task.execute_remotely.task.execute_remotely() -
Download data and store it as an artifact named
dataset. This is the same artifact name used inparameter_overridewhen theadd_stepmethod is called in the pipeline controller.# simulate local dataset, download one, so we have something local local_iris_pkl = StorageManager.get_local_copy( remote_url='https://github.com/allegroai/events/raw/master/odsc20-east/generic/iris_dataset.pkl' ) # add and upload local file containing our toy dataset task.upload_artifact('dataset', artifact_object=local_iris_pkl)
Step 2 - Processing the Data
In the Step 2 Task (step2_data_processing.py):
-
Create a parameter dictionary and connect it to the Task.
args = { 'dataset_task_id': '', 'dataset_url': '', 'random_state': 42, 'test_size': 0.2, } # store arguments, later we will be able to change them from outside the code task.connect(args)The parameter
dataset_urlis the same parameter name used byparameter_overridewhen theadd_stepmethod is called in the pipeline controller. -
Clone base Task and enqueue it for execution using
Task.execute_remotely.task.execute_remotely() -
Later in Step 2, the Task uses the URL in the parameter dictionary to get the data.
iris_pickle = StorageManager.get_local_copy(remote_url=args['dataset_url']) -
Task Processes data and then stores the processed data as artifacts.
task.upload_artifact('X_train', X_train) task.upload_artifact('X_test', X_test) task.upload_artifact('y_train', y_train) task.upload_artifact('y_test', y_test)
Step 3 - Training the Network
In the Step 3 Task (step3_train_model.py):
-
Create a parameter dictionary and connect it to the Task.
# Arguments args = { 'dataset_task_id': 'REPLACE_WITH_DATASET_TASK_ID', } task.connect(args)The parameter
dataset_task_idis later overridden by the ID of the Step 2 Task (cloned Task, not base Task). -
Clone the Step 3 base Task and enqueue it using
Task.execute_remotely.task.execute_remotely() -
Use the Step 2 Task ID to get the processed data stored in artifacts.
dataset_task = Task.get_task(task_id=args['dataset_task_id']) X_train = dataset_task.artifacts['X_train'].get() X_test = dataset_task.artifacts['X_test'].get() y_train = dataset_task.artifacts['y_train'].get() y_test = dataset_task.artifacts['y_test'].get() -
Train the network and log plots, along with ClearML automatic logging.
Running the Pipeline
To run the pipeline:
-
Run the script for each of the steps, if the script has not run once before.
python step1_dataset_artifact.py python step2_data_processing.py python step3_train_model.py -
Run the pipeline controller one of the following two ways:
-
Run the script.
python pipeline_from_tasks.py -
Remotely execute the Task - If the Task
pipeline demoin the projectexamplesalready exists in ClearML Server, clone it and enqueue it to execute.
:::note If you enqueue a Task, make sure an agent is assigned to the queue, so it will execute the Task.
::: -
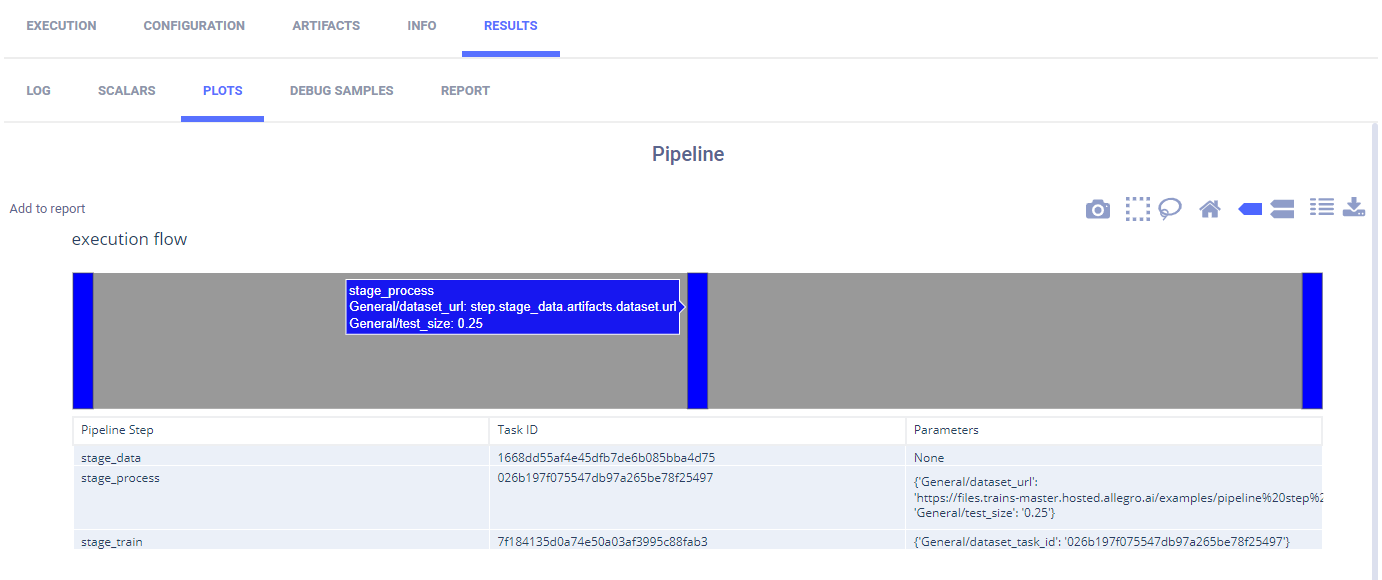
The plot appears in RESULTS > PLOTS describing the pipeline. Hover over a step in the pipeline, and view the name of the step and the parameters overridden by the step.