3.2 KiB
| title |
|---|
| Jupyter Notebook Server Service |
The execute_jupyter_notebook_server.py example demonstrates executing a Jupyter Notebook server in ClearML Agent services mode. The example script creates an SSH server, and runs Jupyter Notebook as a subprocess. We integrate ClearML into the notebooks running on the Jupyter Notebook server by passing environment variables to the subprocess, which point to:
- A ClearML configuration file
- A ClearML Server host configuration (web server, API server, and files server)
- ClearML API credentials.
ClearML logs the server links and console output, including the notebooks run on the server, in the example script's
Task. When the script runs, it creates an experiment named Allocate Jupyter Notebook Instance, which is associated with
the DevOps project in the ClearML Web UI.
Running the Jupyter Notebook server service
-
The example script must run at least once before it can execute as a ClearML Agent service, because the Task must be stored in ClearML Server in order to be enqueued for a ClearML Agent to fetch and execute.
python execute_jupyter_notebook_server.py -
ClearML Agent must be running in services mode and listening to the
servicesqueue.For example:
clearml-agent daemon --services-mode --detached --queue services --create-queue --cpu-only -
Enqueue the Jupyter Notebook server Task.
- In the ClearML Web (UI), Project page > examples project > right click the Remote Jupyter NoteBook experiment.
- In the context menu, click Enqueue > select the services queue > ENQUEUE.
The status changes to Pending and then to Running. Once it is running, the Jupyter Notebook server is ready to run notebooks.
Logging the Jupyter Notebook server
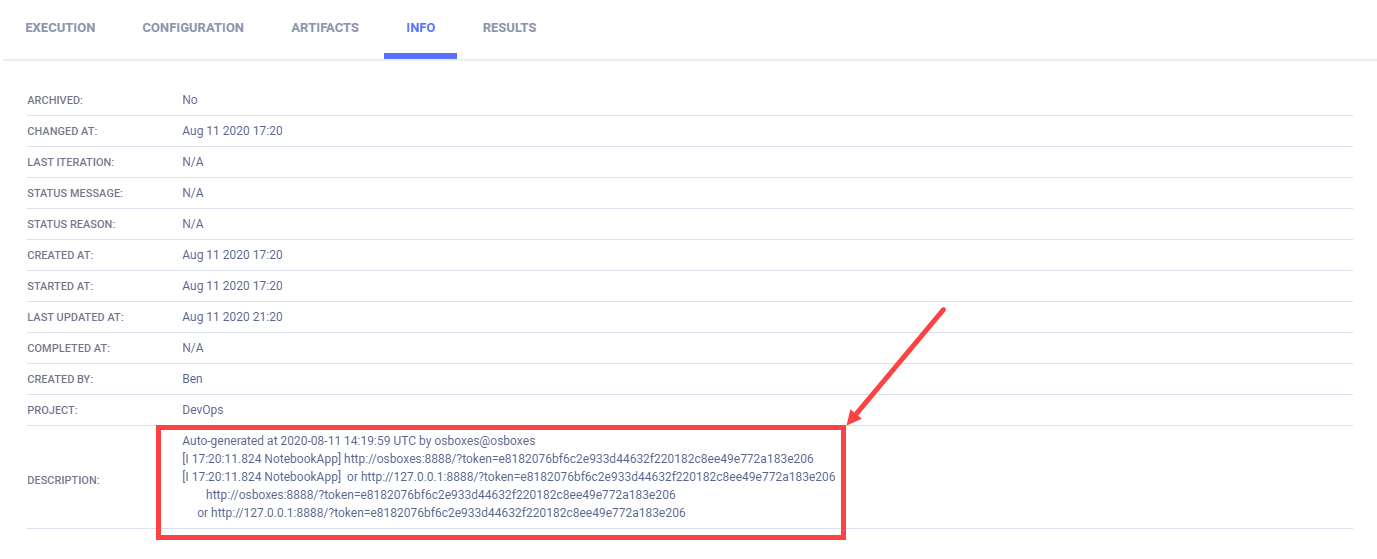
ClearML stores the Jupyter Notebook server links in the Task.comment property, which appears in the ClearML Web UI
> the experiment's INFO tab > DESCRIPTION section.
task.comment += "\n" + "".join(
line for line in new_lines if "http://" in line or "https://" in line
)
It shows the server links are:
[I 12:54:48.940 NotebookApp] http://osboxes:8889/?token=3be82d87e83268934dd086e3b136cc408d4bd12e23409f3a
[I 12:54:48.940 NotebookApp] or http://127.0.0.1:8889/?token=3be82d87e83268934dd086e3b136cc408d4bd12e23409f3a
http://osboxes:8889/?token=3be82d87e83268934dd086e3b136cc408d4bd12e23409f3a
or http://127.0.0.1:8889/?token=3be82d87e83268934dd086e3b136cc408d4bd12e23409f3a
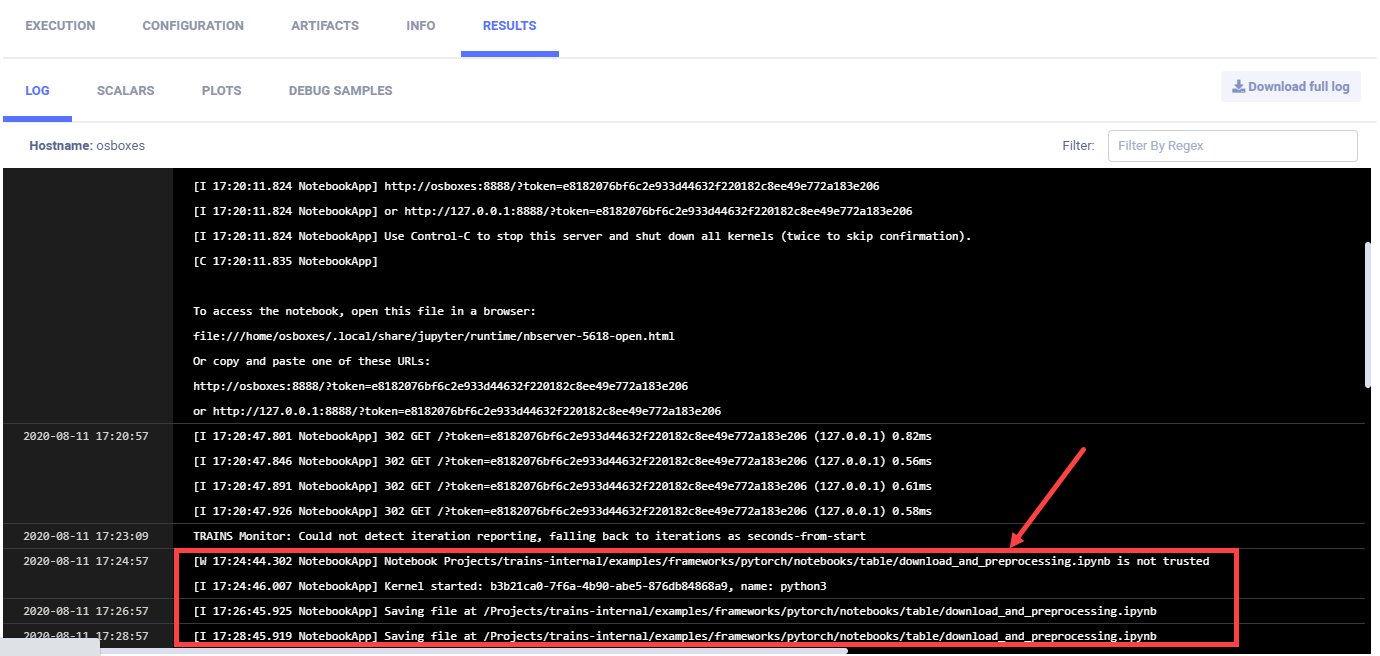
The Jupyter Note Server console output appears in RESULTS > LOG, including log entries for the notebooks run on the server.
To test the Jupyter Notebook, we ran a notebook named audio_preprocessing_example.ipynb. The log shows it was saved:
[I 17:26:45.925 NotebookApp] Saving file at /Projects/clearml-internal/examples/frameworks/pytorch/notebooks/table/download_and_preprocessing.ipynb