

[ Homepage] | [🤖 Chat with DeepSeek Coder] | [🤗 Models Download] | [Discord] | [Wechat(微信)]
Homepage] | [🤖 Chat with DeepSeek Coder] | [🤗 Models Download] | [Discord] | [Wechat(微信)]
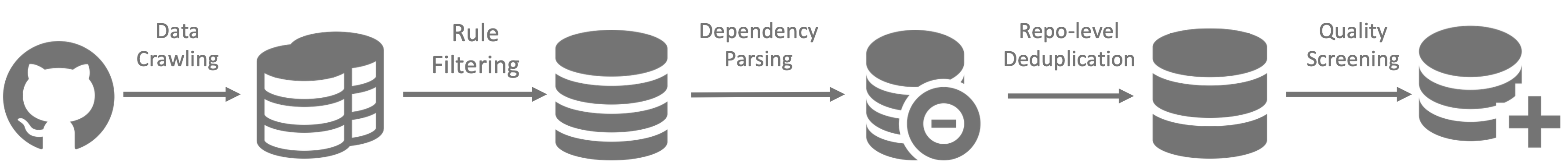 #### Model Training
- Step 1: Initially pre-trained with a dataset consisting of 87% code, 10% code-related language (Github Markdown and StackExchange), and 3% non-code related Chinese language. Models are pre-trained using 1.8T tokens and a 4K window size in this step.
- Step 2: Further Pre-training using an extended 16K window size on an additional 200B tokens, resulting in foundational models (**DeepSeek-Coder-Base**).
- Step 3: Instruction Fine-tuning on 2B tokens of instruction data, resulting in instruction-tuned models (**DeepSeek-Coder-Instruct**).
#### Model Training
- Step 1: Initially pre-trained with a dataset consisting of 87% code, 10% code-related language (Github Markdown and StackExchange), and 3% non-code related Chinese language. Models are pre-trained using 1.8T tokens and a 4K window size in this step.
- Step 2: Further Pre-training using an extended 16K window size on an additional 200B tokens, resulting in foundational models (**DeepSeek-Coder-Base**).
- Step 3: Instruction Fine-tuning on 2B tokens of instruction data, resulting in instruction-tuned models (**DeepSeek-Coder-Instruct**).
 ### 4. How to Use
Before proceeding, you'll need to install the necessary dependencies. You can do this by running the following command:
```
pip install -r requirements.txt
```
A demo is also available on the [🤗 Hugging Face Space](https://huggingface.co/spaces/deepseek-ai/deepseek-coder-7b-instruct), and you can run the demo locally using `app.py` in [demo](https://github.com/deepseek-ai/deepseek-coder/tree/main/demo) folder. (Thanks to all the HF team for their support)
Here are some examples of how to use our model.
#### 1)Code Completion
```python
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM
import torch
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("deepseek-ai/deepseek-coder-6.7b-base", trust_remote_code=True)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("deepseek-ai/deepseek-coder-6.7b-base", trust_remote_code=True).cuda()
input_text = "#write a quick sort algorithm"
inputs = tokenizer(input_text, return_tensors="pt").to(model.device)
outputs = model.generate(**inputs, max_length=128)
print(tokenizer.decode(outputs[0], skip_special_tokens=True))
```
This code will output the following result:
```
def quick_sort(arr):
if len(arr) <= 1:
return arr
pivot = arr[0]
left = []
right = []
for i in range(1, len(arr)):
if arr[i] < pivot:
left.append(arr[i])
else:
right.append(arr[i])
return quick_sort(left) + [pivot] + quick_sort(right)
```
#### 2)Code Insertion
```python
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM
import torch
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("deepseek-ai/deepseek-coder-6.7b-base", trust_remote_code=True)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("deepseek-ai/deepseek-coder-6.7b-base", trust_remote_code=True).cuda()
input_text = """<|fim▁begin|>def quick_sort(arr):
if len(arr) <= 1:
return arr
pivot = arr[0]
left = []
right = []
<|fim▁hole|>
if arr[i] < pivot:
left.append(arr[i])
else:
right.append(arr[i])
return quick_sort(left) + [pivot] + quick_sort(right)<|fim▁end|>"""
inputs = tokenizer(input_text, return_tensors="pt").to(model.device)
outputs = model.generate(**inputs, max_length=128)
print(tokenizer.decode(outputs[0], skip_special_tokens=True)[len(input_text):])
```
This code will output the following result:
```
for i in range(1, len(arr)):
```
#### 3)Chat Model Inference
```python
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("deepseek-ai/deepseek-coder-6.7b-instruct", trust_remote_code=True)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("deepseek-ai/deepseek-coder-6.7b-instruct", trust_remote_code=True).cuda()
messages=[
{ 'role': 'user', 'content': "write a quick sort algorithm in python."}
]
inputs = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(messages, return_tensors="pt").to(model.device)
# 32021 is the id of <|EOT|> token
outputs = model.generate(inputs, max_new_tokens=512, do_sample=False, top_k=50, top_p=0.95, num_return_sequences=1, eos_token_id=32021)
print(tokenizer.decode(outputs[0][len(inputs[0]):], skip_special_tokens=True))
```
This code will output the following result:
```
Sure, here is a simple implementation of the Quick Sort algorithm in Python:
def quick_sort(arr):
if len(arr) <= 1:
return arr
else:
pivot = arr[0]
less_than_pivot = [x for x in arr[1:] if x <= pivot]
greater_than_pivot = [x for x in arr[1:] if x > pivot]
return quick_sort(less_than_pivot) + [pivot] + quick_sort(greater_than_pivot)
# Test the function
arr = [10, 7, 8, 9, 1, 5]
print("Original array:", arr)
print("Sorted array:", quick_sort(arr))
This code works by selecting a 'pivot' element from the array and partitioning the other elements into two sub-arrays, according to whether they are less than or greater than the pivot. The pivot element is then in its final position. The process is then repeated for the sub-arrays.
```
#### 4)Repository Level Code Completion
```python
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("deepseek-ai/deepseek-coder-6.7b-base", trust_remote_code=True)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("deepseek-ai/deepseek-coder-6.7b-base", trust_remote_code=True).cuda()
input_text = """#utils.py
import torch
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
def load_data():
iris = datasets.load_iris()
X = iris.data
y = iris.target
# Standardize the data
scaler = StandardScaler()
X = scaler.fit_transform(X)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.3, random_state=42)
# Convert numpy data to PyTorch tensors
X_train = torch.tensor(X_train, dtype=torch.float32)
X_test = torch.tensor(X_test, dtype=torch.float32)
y_train = torch.tensor(y_train, dtype=torch.int64)
y_test = torch.tensor(y_test, dtype=torch.int64)
return X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test
def evaluate_predictions(y_test, y_pred):
return accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred)
#model.py
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader, TensorDataset
class IrisClassifier(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(IrisClassifier, self).__init__()
self.fc = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(4, 16),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(16, 3)
)
def forward(self, x):
return self.fc(x)
def train_model(self, X_train, y_train, epochs, lr, batch_size):
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = optim.Adam(self.parameters(), lr=lr)
# Create DataLoader for batches
dataset = TensorDataset(X_train, y_train)
dataloader = DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True)
for epoch in range(epochs):
for batch_X, batch_y in dataloader:
optimizer.zero_grad()
outputs = self(batch_X)
loss = criterion(outputs, batch_y)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
def predict(self, X_test):
with torch.no_grad():
outputs = self(X_test)
_, predicted = outputs.max(1)
return predicted.numpy()
#main.py
from utils import load_data, evaluate_predictions
from model import IrisClassifier as Classifier
def main():
# Model training and evaluation
"""
inputs = tokenizer(input_text, return_tensors="pt").to(model.device)
outputs = model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=140)
print(tokenizer.decode(outputs[0]))
```
---
In the following scenario, the Deepseek-Coder 6.7B model effectively calls a class **IrisClassifier** and its member function from the `model.py` file, and also utilizes functions from the `utils.py` file, to correctly complete the **main** function in`main.py` file for model training and evaluation.

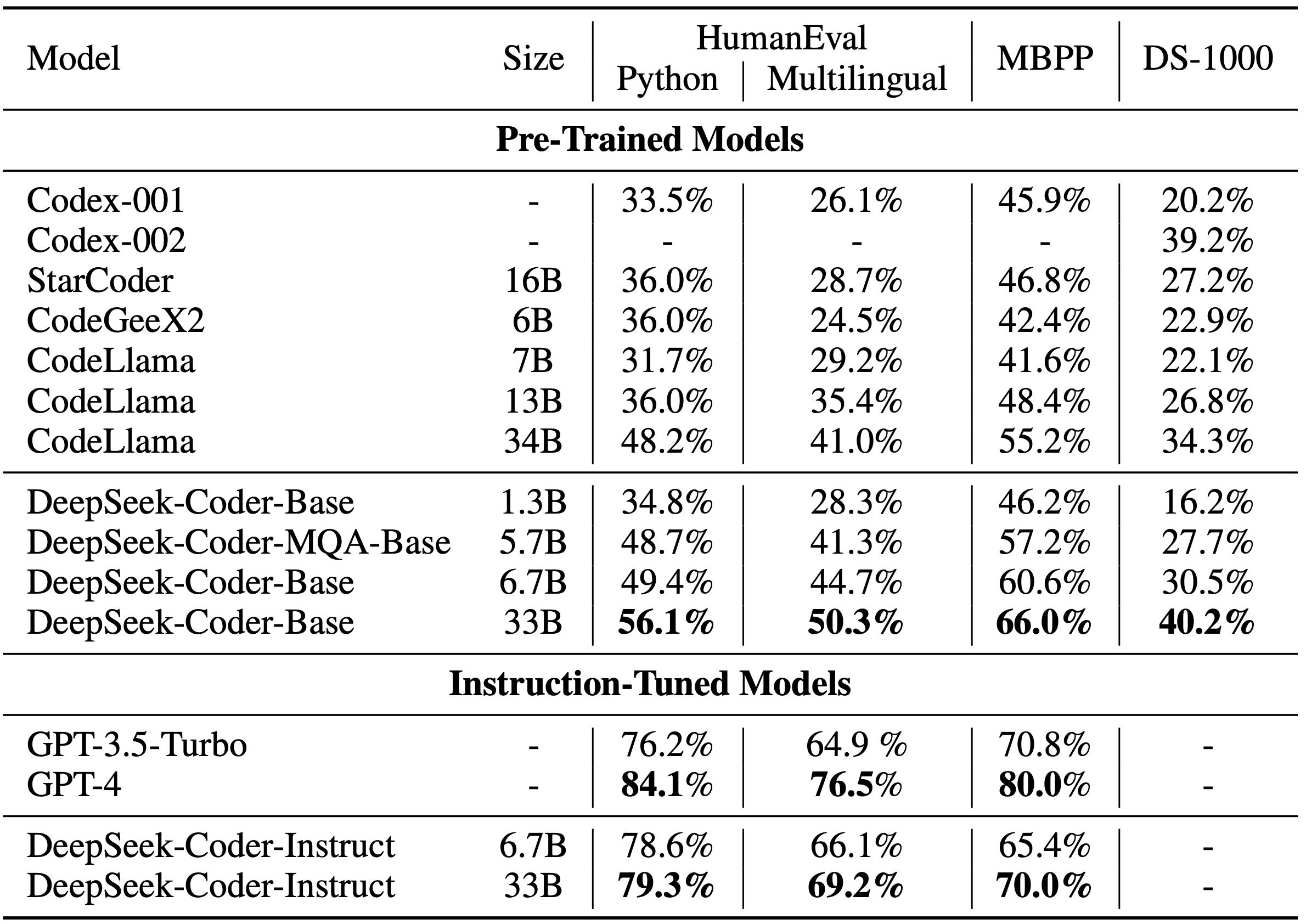
### 5. Detailed Evaluation Results
The reproducible code for the following evaluation results can be found in the [Evaluation](https://github.com/deepseek-ai/deepseek-coder/tree/main/Evaluation) directory.
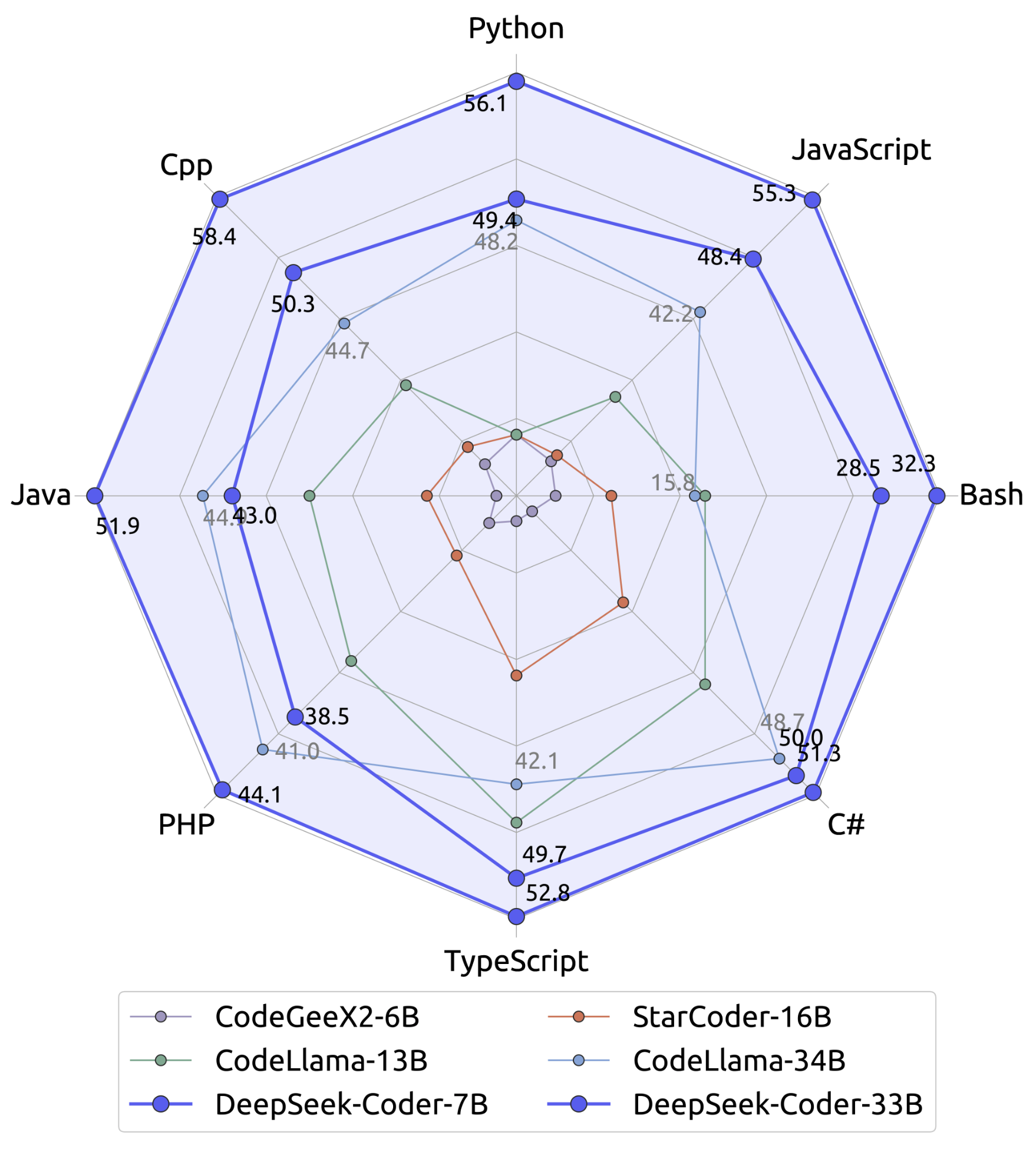
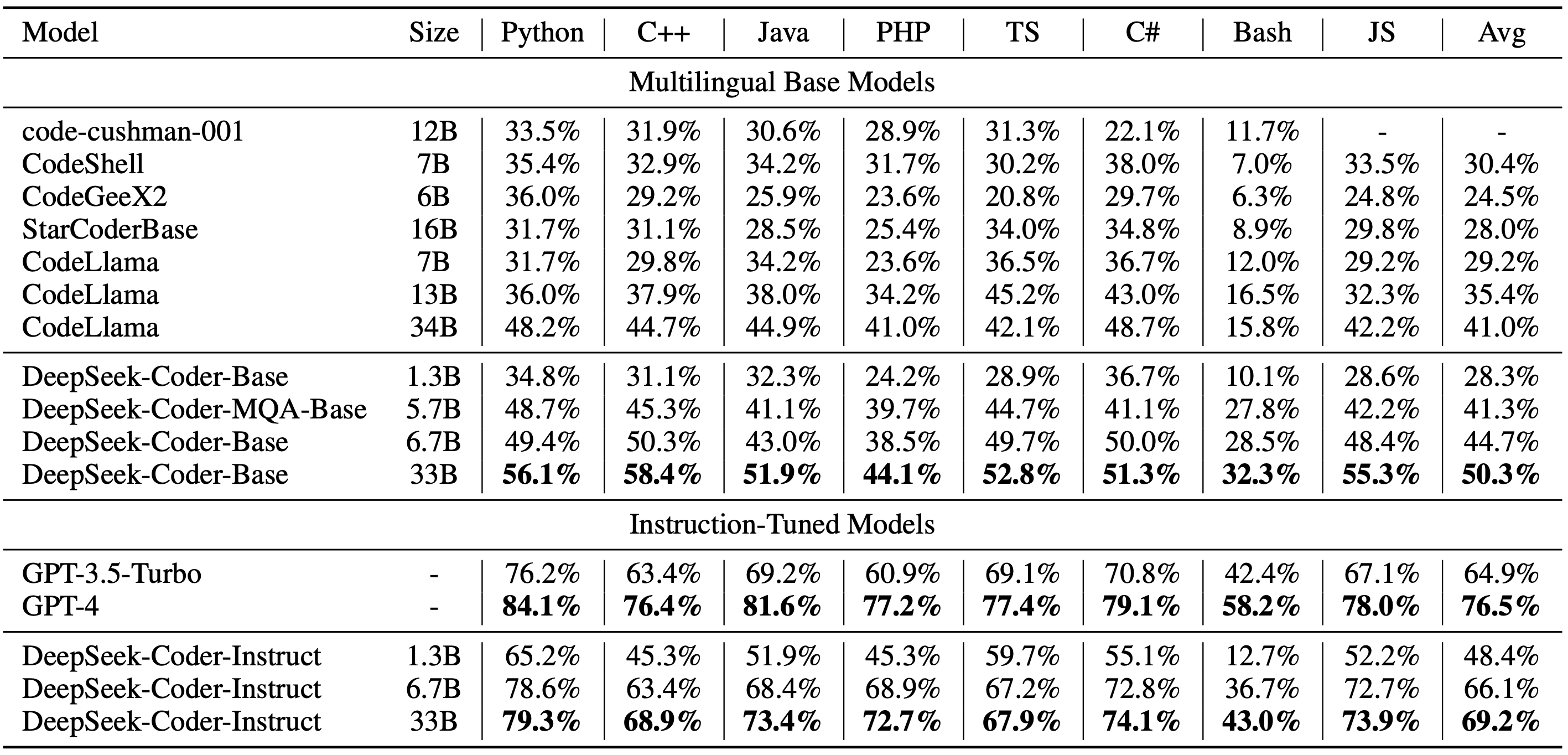
#### 1)Multilingual HumanEval Benchmark
#### 2)MBPP Benchmark
### 4. How to Use
Before proceeding, you'll need to install the necessary dependencies. You can do this by running the following command:
```
pip install -r requirements.txt
```
A demo is also available on the [🤗 Hugging Face Space](https://huggingface.co/spaces/deepseek-ai/deepseek-coder-7b-instruct), and you can run the demo locally using `app.py` in [demo](https://github.com/deepseek-ai/deepseek-coder/tree/main/demo) folder. (Thanks to all the HF team for their support)
Here are some examples of how to use our model.
#### 1)Code Completion
```python
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM
import torch
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("deepseek-ai/deepseek-coder-6.7b-base", trust_remote_code=True)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("deepseek-ai/deepseek-coder-6.7b-base", trust_remote_code=True).cuda()
input_text = "#write a quick sort algorithm"
inputs = tokenizer(input_text, return_tensors="pt").to(model.device)
outputs = model.generate(**inputs, max_length=128)
print(tokenizer.decode(outputs[0], skip_special_tokens=True))
```
This code will output the following result:
```
def quick_sort(arr):
if len(arr) <= 1:
return arr
pivot = arr[0]
left = []
right = []
for i in range(1, len(arr)):
if arr[i] < pivot:
left.append(arr[i])
else:
right.append(arr[i])
return quick_sort(left) + [pivot] + quick_sort(right)
```
#### 2)Code Insertion
```python
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM
import torch
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("deepseek-ai/deepseek-coder-6.7b-base", trust_remote_code=True)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("deepseek-ai/deepseek-coder-6.7b-base", trust_remote_code=True).cuda()
input_text = """<|fim▁begin|>def quick_sort(arr):
if len(arr) <= 1:
return arr
pivot = arr[0]
left = []
right = []
<|fim▁hole|>
if arr[i] < pivot:
left.append(arr[i])
else:
right.append(arr[i])
return quick_sort(left) + [pivot] + quick_sort(right)<|fim▁end|>"""
inputs = tokenizer(input_text, return_tensors="pt").to(model.device)
outputs = model.generate(**inputs, max_length=128)
print(tokenizer.decode(outputs[0], skip_special_tokens=True)[len(input_text):])
```
This code will output the following result:
```
for i in range(1, len(arr)):
```
#### 3)Chat Model Inference
```python
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("deepseek-ai/deepseek-coder-6.7b-instruct", trust_remote_code=True)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("deepseek-ai/deepseek-coder-6.7b-instruct", trust_remote_code=True).cuda()
messages=[
{ 'role': 'user', 'content': "write a quick sort algorithm in python."}
]
inputs = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(messages, return_tensors="pt").to(model.device)
# 32021 is the id of <|EOT|> token
outputs = model.generate(inputs, max_new_tokens=512, do_sample=False, top_k=50, top_p=0.95, num_return_sequences=1, eos_token_id=32021)
print(tokenizer.decode(outputs[0][len(inputs[0]):], skip_special_tokens=True))
```
This code will output the following result:
```
Sure, here is a simple implementation of the Quick Sort algorithm in Python:
def quick_sort(arr):
if len(arr) <= 1:
return arr
else:
pivot = arr[0]
less_than_pivot = [x for x in arr[1:] if x <= pivot]
greater_than_pivot = [x for x in arr[1:] if x > pivot]
return quick_sort(less_than_pivot) + [pivot] + quick_sort(greater_than_pivot)
# Test the function
arr = [10, 7, 8, 9, 1, 5]
print("Original array:", arr)
print("Sorted array:", quick_sort(arr))
This code works by selecting a 'pivot' element from the array and partitioning the other elements into two sub-arrays, according to whether they are less than or greater than the pivot. The pivot element is then in its final position. The process is then repeated for the sub-arrays.
```
#### 4)Repository Level Code Completion
```python
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("deepseek-ai/deepseek-coder-6.7b-base", trust_remote_code=True)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("deepseek-ai/deepseek-coder-6.7b-base", trust_remote_code=True).cuda()
input_text = """#utils.py
import torch
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
def load_data():
iris = datasets.load_iris()
X = iris.data
y = iris.target
# Standardize the data
scaler = StandardScaler()
X = scaler.fit_transform(X)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.3, random_state=42)
# Convert numpy data to PyTorch tensors
X_train = torch.tensor(X_train, dtype=torch.float32)
X_test = torch.tensor(X_test, dtype=torch.float32)
y_train = torch.tensor(y_train, dtype=torch.int64)
y_test = torch.tensor(y_test, dtype=torch.int64)
return X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test
def evaluate_predictions(y_test, y_pred):
return accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred)
#model.py
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader, TensorDataset
class IrisClassifier(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(IrisClassifier, self).__init__()
self.fc = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(4, 16),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(16, 3)
)
def forward(self, x):
return self.fc(x)
def train_model(self, X_train, y_train, epochs, lr, batch_size):
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = optim.Adam(self.parameters(), lr=lr)
# Create DataLoader for batches
dataset = TensorDataset(X_train, y_train)
dataloader = DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True)
for epoch in range(epochs):
for batch_X, batch_y in dataloader:
optimizer.zero_grad()
outputs = self(batch_X)
loss = criterion(outputs, batch_y)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
def predict(self, X_test):
with torch.no_grad():
outputs = self(X_test)
_, predicted = outputs.max(1)
return predicted.numpy()
#main.py
from utils import load_data, evaluate_predictions
from model import IrisClassifier as Classifier
def main():
# Model training and evaluation
"""
inputs = tokenizer(input_text, return_tensors="pt").to(model.device)
outputs = model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=140)
print(tokenizer.decode(outputs[0]))
```
---
In the following scenario, the Deepseek-Coder 6.7B model effectively calls a class **IrisClassifier** and its member function from the `model.py` file, and also utilizes functions from the `utils.py` file, to correctly complete the **main** function in`main.py` file for model training and evaluation.

### 5. Detailed Evaluation Results
The reproducible code for the following evaluation results can be found in the [Evaluation](https://github.com/deepseek-ai/deepseek-coder/tree/main/Evaluation) directory.
#### 1)Multilingual HumanEval Benchmark

#### 2)MBPP Benchmark
 #### 3)DS-1000 Benchmark

#### 4)Program-Aid Math Reasoning Benchmark
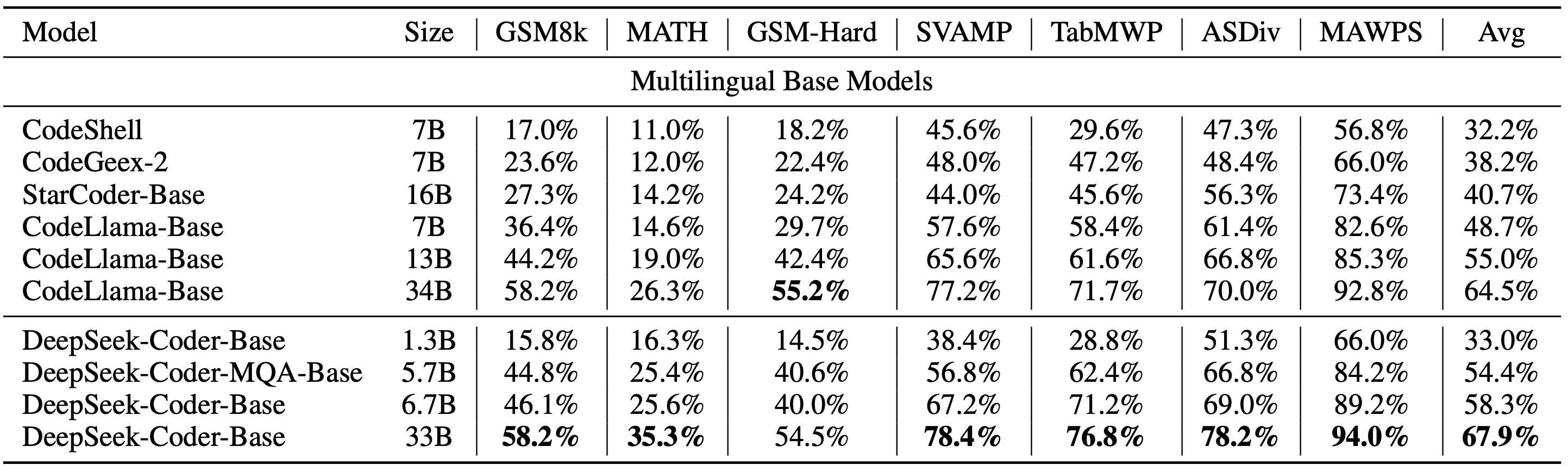
### 6. License
This code repository is licensed under the MIT License. The use of DeepSeek Coder models is subject to the Model License. DeepSeek Coder supports commercial use.
See the [LICENSE-CODE](LICENSE-CODE) and [LICENSE-MODEL](LICENSE-MODEL) for more details.
### 6. Contact
If you have any questions, please raise an issue or contact us at [agi_code@deepseek.com](mailto:agi_code@deepseek.com).
#### 3)DS-1000 Benchmark

#### 4)Program-Aid Math Reasoning Benchmark

### 6. License
This code repository is licensed under the MIT License. The use of DeepSeek Coder models is subject to the Model License. DeepSeek Coder supports commercial use.
See the [LICENSE-CODE](LICENSE-CODE) and [LICENSE-MODEL](LICENSE-MODEL) for more details.
### 6. Contact
If you have any questions, please raise an issue or contact us at [agi_code@deepseek.com](mailto:agi_code@deepseek.com).