

[ Homepage] | [🤖 Chat with DeepSeek Coder] | [🤗 Models Download] | [Discord] | [WeChat (微信)]
Homepage] | [🤖 Chat with DeepSeek Coder] | [🤗 Models Download] | [Discord] | [WeChat (微信)]
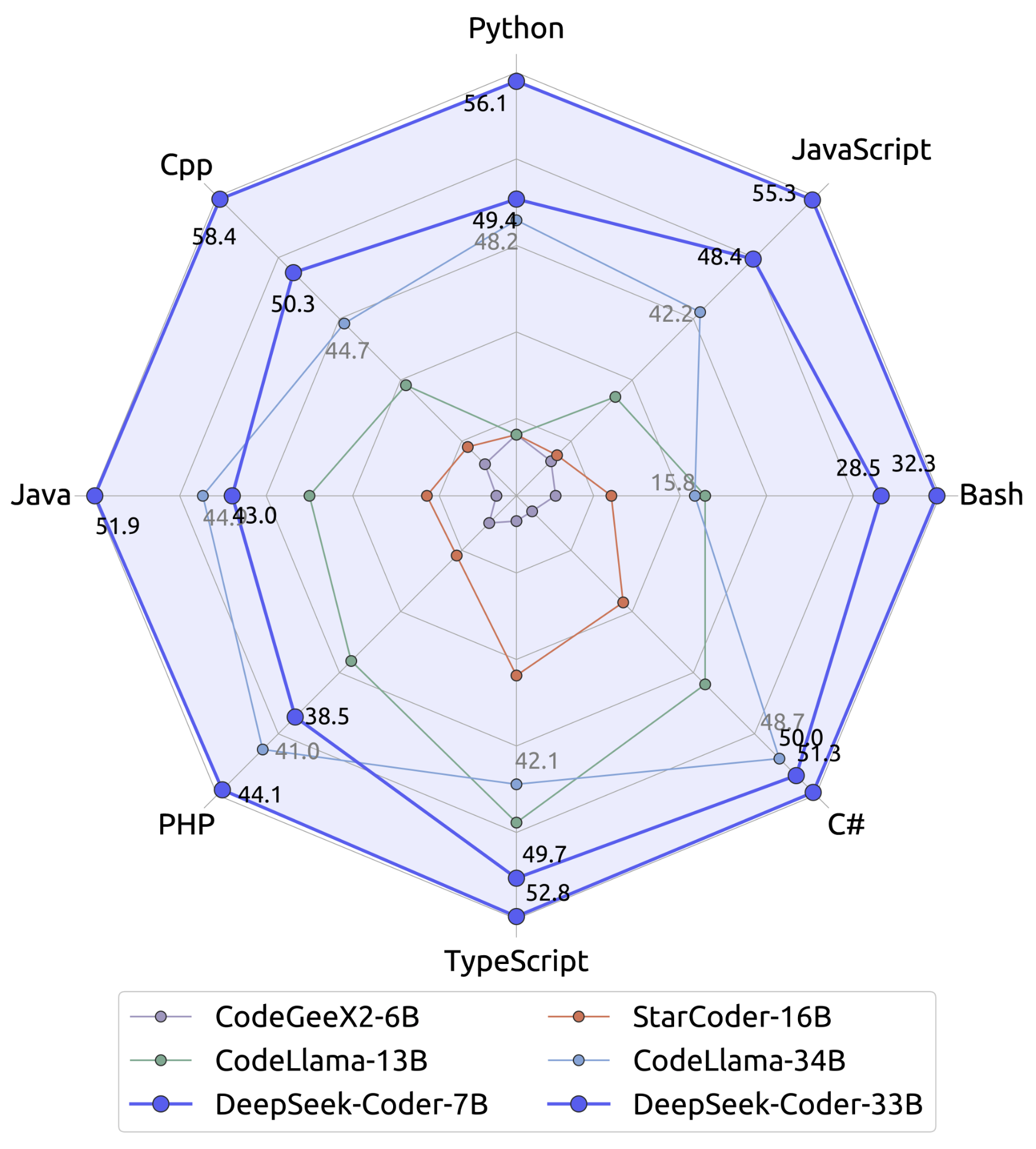
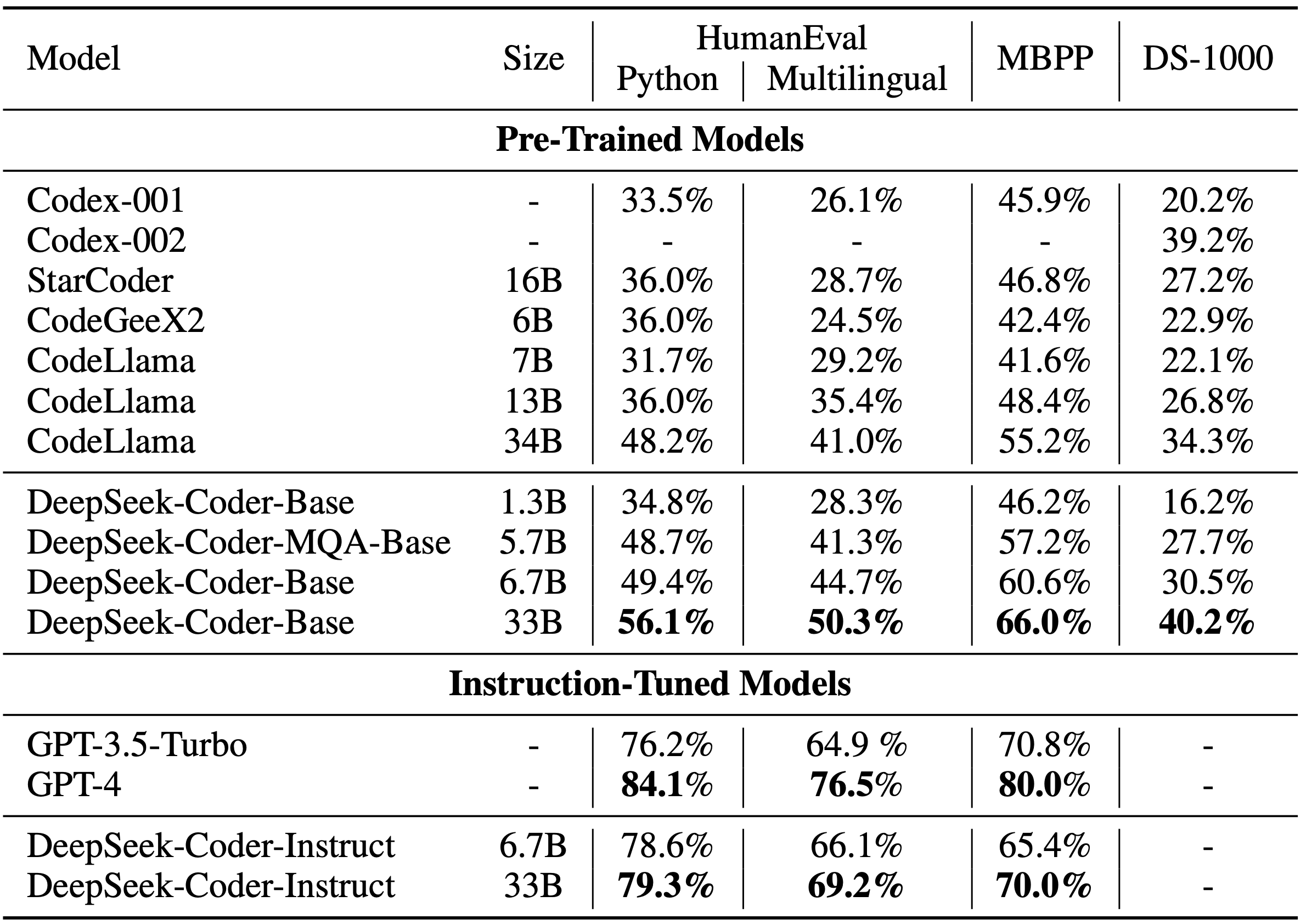
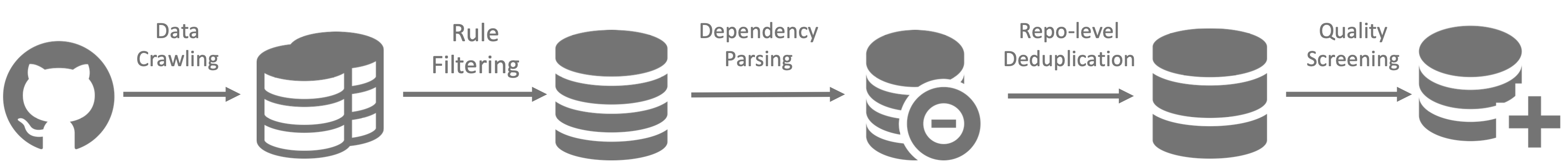 #### Model Training
- Step 1: Initially pre-trained with a dataset consisting of 87% code, 10% code-related language (Github Markdown and StackExchange), and 3% non-code-related Chinese language. Models are pre-trained using 1.8T tokens and a 4K window size in this step.
- Step 2: Further Pre-training using an extended 16K window size on an additional 200B tokens, resulting in foundational models (**DeepSeek-Coder-Base**).
- Step 3: Instruction Fine-tuning on 2B tokens of instruction data, resulting in instruction-tuned models (**DeepSeek-Coder-Instruct**).
#### Model Training
- Step 1: Initially pre-trained with a dataset consisting of 87% code, 10% code-related language (Github Markdown and StackExchange), and 3% non-code-related Chinese language. Models are pre-trained using 1.8T tokens and a 4K window size in this step.
- Step 2: Further Pre-training using an extended 16K window size on an additional 200B tokens, resulting in foundational models (**DeepSeek-Coder-Base**).
- Step 3: Instruction Fine-tuning on 2B tokens of instruction data, resulting in instruction-tuned models (**DeepSeek-Coder-Instruct**).
 ### 4. How to Use
Before proceeding, you'll need to install the necessary dependencies. You can do this by running the following command:
```
pip install -r requirements.txt
```
A demo is also available on the [🤗 Hugging Face Space](https://huggingface.co/spaces/deepseek-ai/deepseek-coder-33b-instruct), and you can run the demo locally using `app.py` in the [demo](https://github.com/deepseek-ai/deepseek-coder/tree/main/demo) folder. (Thanks to all the HF team for their support)
Here are some examples of how to use our model.
#### 1) Code Completion
```python
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM
import torch
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("deepseek-ai/deepseek-coder-6.7b-base", trust_remote_code=True)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("deepseek-ai/deepseek-coder-6.7b-base", trust_remote_code=True, torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16).cuda()
input_text = "#write a quick sort algorithm"
inputs = tokenizer(input_text, return_tensors="pt").to(model.device)
outputs = model.generate(**inputs, max_length=128)
print(tokenizer.decode(outputs[0], skip_special_tokens=True))
```
This code will output the following result:
```
def quick_sort(arr):
if len(arr) <= 1:
return arr
pivot = arr[0]
left = []
right = []
for i in range(1, len(arr)):
if arr[i] < pivot:
left.append(arr[i])
else:
right.append(arr[i])
return quick_sort(left) + [pivot] + quick_sort(right)
```
#### 2) Code Insertion
```python
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM
import torch
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("deepseek-ai/deepseek-coder-6.7b-base", trust_remote_code=True)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("deepseek-ai/deepseek-coder-6.7b-base", trust_remote_code=True, torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16).cuda()
input_text = """<|fim▁begin|>def quick_sort(arr):
if len(arr) <= 1:
return arr
pivot = arr[0]
left = []
right = []
<|fim▁hole|>
if arr[i] < pivot:
left.append(arr[i])
else:
right.append(arr[i])
return quick_sort(left) + [pivot] + quick_sort(right)<|fim▁end|>"""
inputs = tokenizer(input_text, return_tensors="pt").to(model.device)
outputs = model.generate(**inputs, max_length=128)
print(tokenizer.decode(outputs[0], skip_special_tokens=True)[len(input_text):])
```
This code will output the following result:
```
for i in range(1, len(arr)):
```
#### 3) Chat Model Inference
```python
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM
import torch
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("deepseek-ai/deepseek-coder-6.7b-instruct", trust_remote_code=True)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("deepseek-ai/deepseek-coder-6.7b-instruct", trust_remote_code=True, torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16).cuda()
messages=[
{ 'role': 'user', 'content': "write a quick sort algorithm in python."}
]
inputs = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(messages, add_generation_prompt=True, return_tensors="pt").to(model.device)
# tokenizer.eos_token_id is the id of <|EOT|> token
outputs = model.generate(inputs, max_new_tokens=512, do_sample=False, top_k=50, top_p=0.95, num_return_sequences=1, eos_token_id=tokenizer.eos_token_id)
print(tokenizer.decode(outputs[0][len(inputs[0]):], skip_special_tokens=True))
```
This code will output the following result:
```
Sure, here is a simple implementation of the Quick Sort algorithm in Python:
def quick_sort(arr):
if len(arr) <= 1:
return arr
else:
pivot = arr[0]
less_than_pivot = [x for x in arr[1:] if x <= pivot]
greater_than_pivot = [x for x in arr[1:] if x > pivot]
return quick_sort(less_than_pivot) + [pivot] + quick_sort(greater_than_pivot)
# Test the function
arr = [10, 7, 8, 9, 1, 5]
print("Original array:", arr)
print("Sorted array:", quick_sort(arr))
This code works by selecting a 'pivot' element from the array and partitioning the other elements into two sub-arrays, according to whether they are less than or greater than the pivot. The pivot element is then in its final position. The process is then repeated for the sub-arrays.
```
If you don't want to use the provided API `apply_chat_template` which loads the template from `tokenizer_config.json`, you can use the following template to chat with our model. Replace the `['content']` with your instructions and the model's previous (if any) responses, then the model will generate the response to the currently given instruction.
```
You are an AI programming assistant, utilizing the DeepSeek Coder model, developed by DeepSeek Company, and you only answer questions related to computer science. For politically sensitive questions, security and privacy issues, and other non-computer science questions, you will refuse to answer.
### Instruction:
['content']
### Response:
['content']
<|EOT|>
### Instruction:
['content']
### Response:
```
#### 4) Repository Level Code Completion
```python
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM
import torch
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("deepseek-ai/deepseek-coder-6.7b-base", trust_remote_code=True)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("deepseek-ai/deepseek-coder-6.7b-base", trust_remote_code=True, torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16).cuda()
input_text = """#utils.py
import torch
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
def load_data():
iris = datasets.load_iris()
X = iris.data
y = iris.target
# Standardize the data
scaler = StandardScaler()
X = scaler.fit_transform(X)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.3, random_state=42)
# Convert numpy data to PyTorch tensors
X_train = torch.tensor(X_train, dtype=torch.float32)
X_test = torch.tensor(X_test, dtype=torch.float32)
y_train = torch.tensor(y_train, dtype=torch.int64)
y_test = torch.tensor(y_test, dtype=torch.int64)
return X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test
def evaluate_predictions(y_test, y_pred):
return accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred)
# model.py
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader, TensorDataset
class IrisClassifier(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(IrisClassifier, self).__init__()
self.fc = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(4, 16),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(16, 3)
)
def forward(self, x):
return self.fc(x)
def train_model(self, X_train, y_train, epochs, lr, batch_size):
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = optim.Adam(self.parameters(), lr=lr)
# Create DataLoader for batches
dataset = TensorDataset(X_train, y_train)
dataloader = DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True)
for epoch in range(epochs):
for batch_X, batch_y in dataloader:
optimizer.zero_grad()
outputs = self(batch_X)
loss = criterion(outputs, batch_y)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
def predict(self, X_test):
with torch.no_grad():
outputs = self(X_test)
_, predicted = outputs.max(1)
return predicted.numpy()
# main.py
from utils import load_data, evaluate_predictions
from model import IrisClassifier as Classifier
def main():
# Model training and evaluation
"""
inputs = tokenizer(input_text, return_tensors="pt").to(model.device)
outputs = model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=140)
print(tokenizer.decode(outputs[0]))
```
---
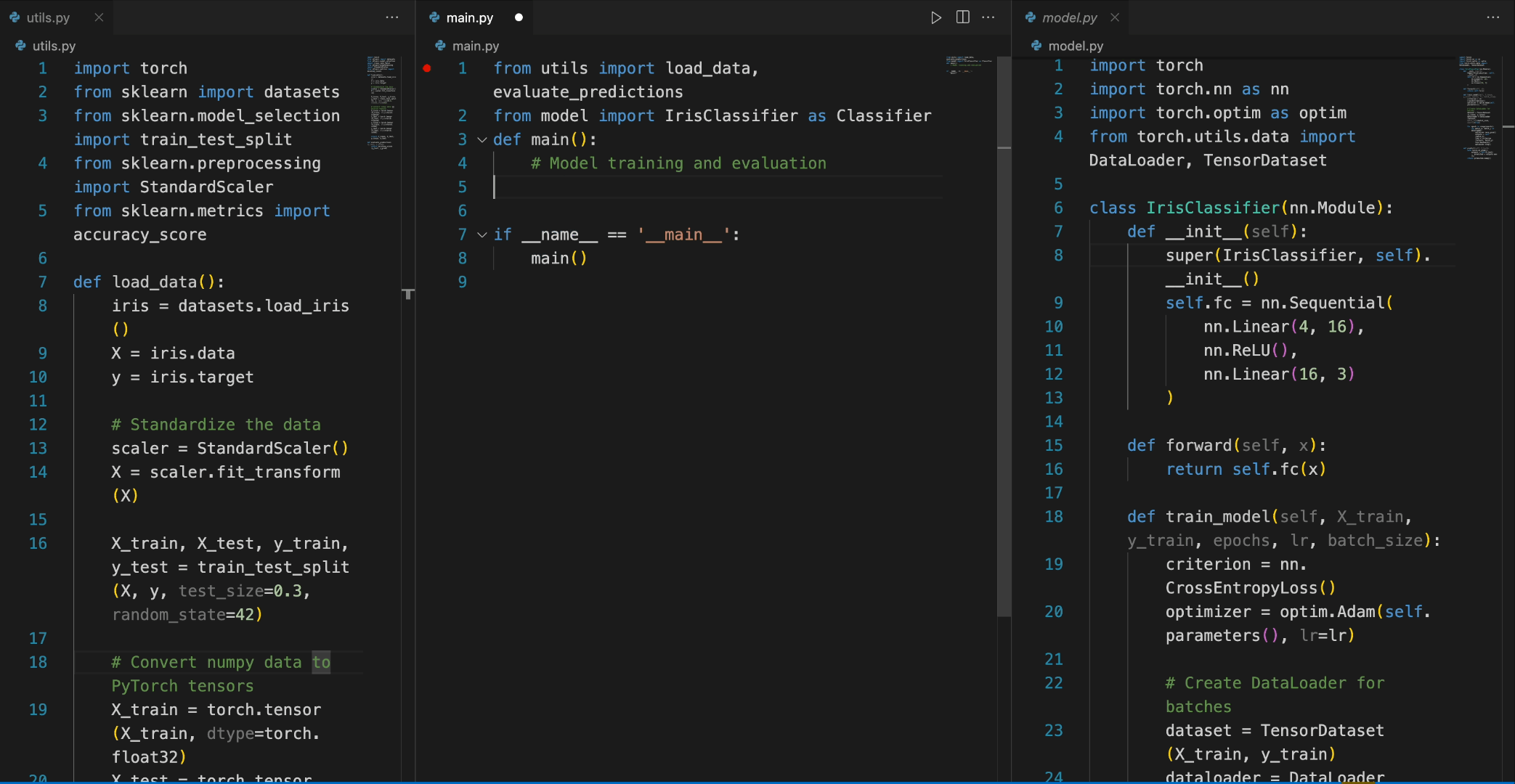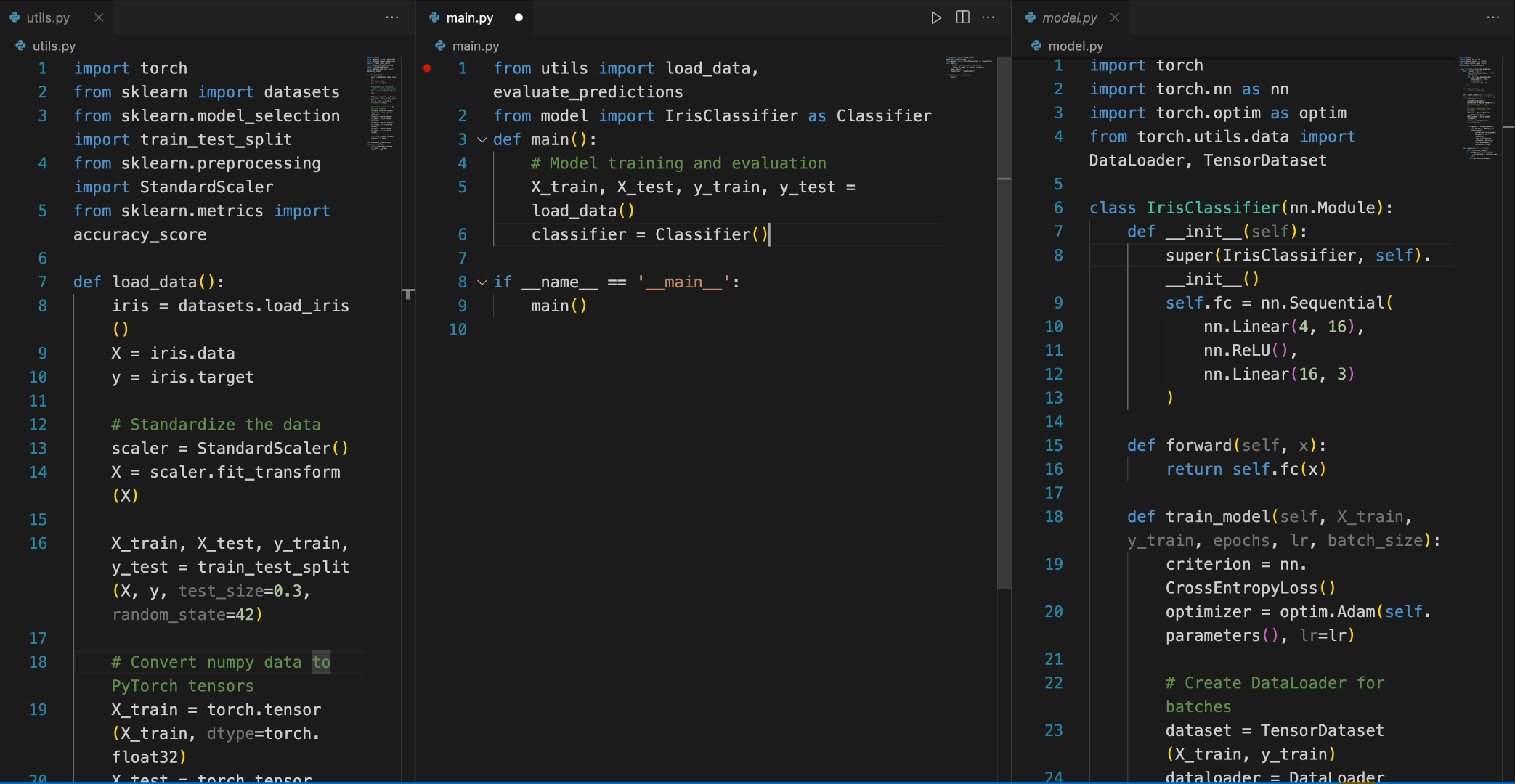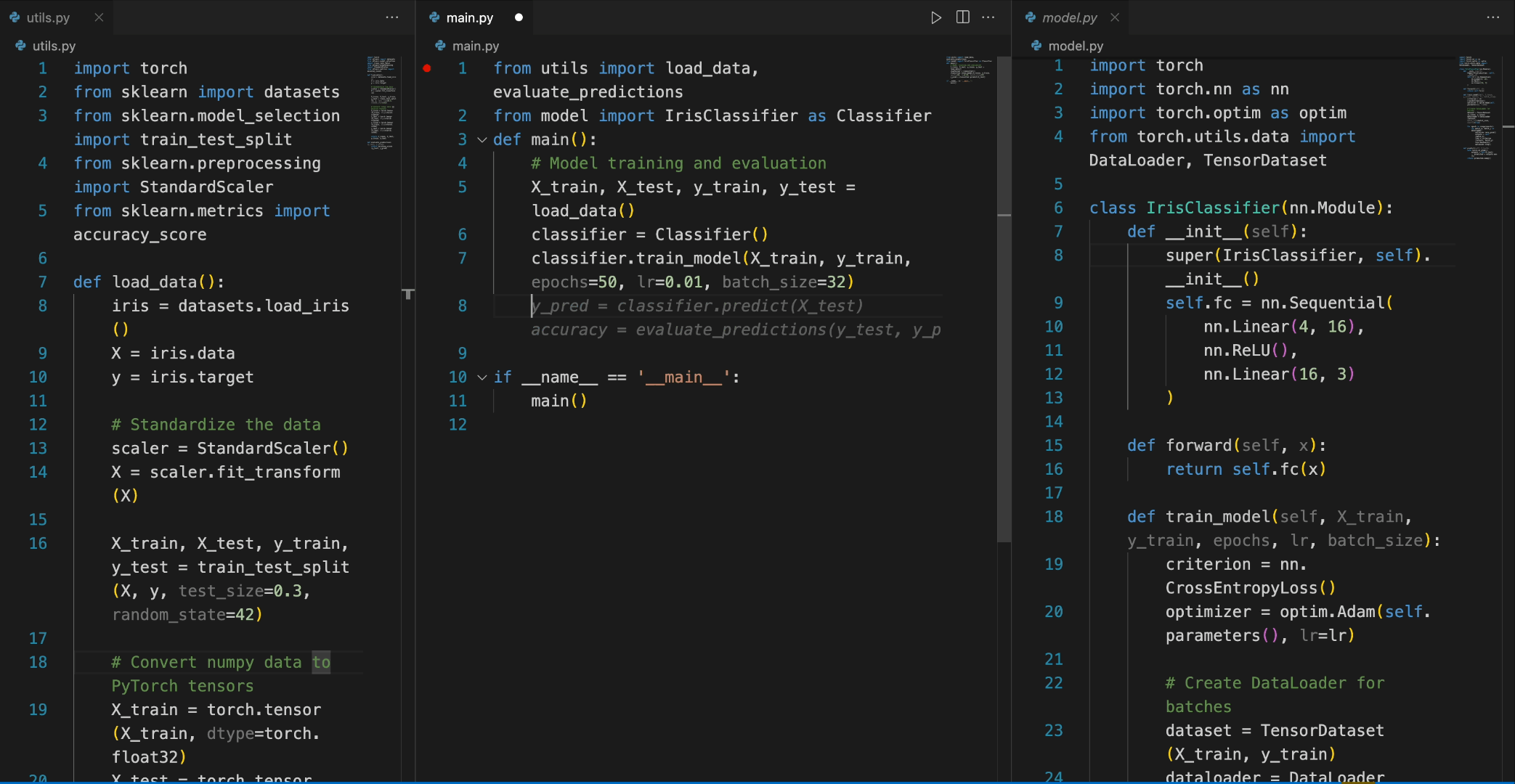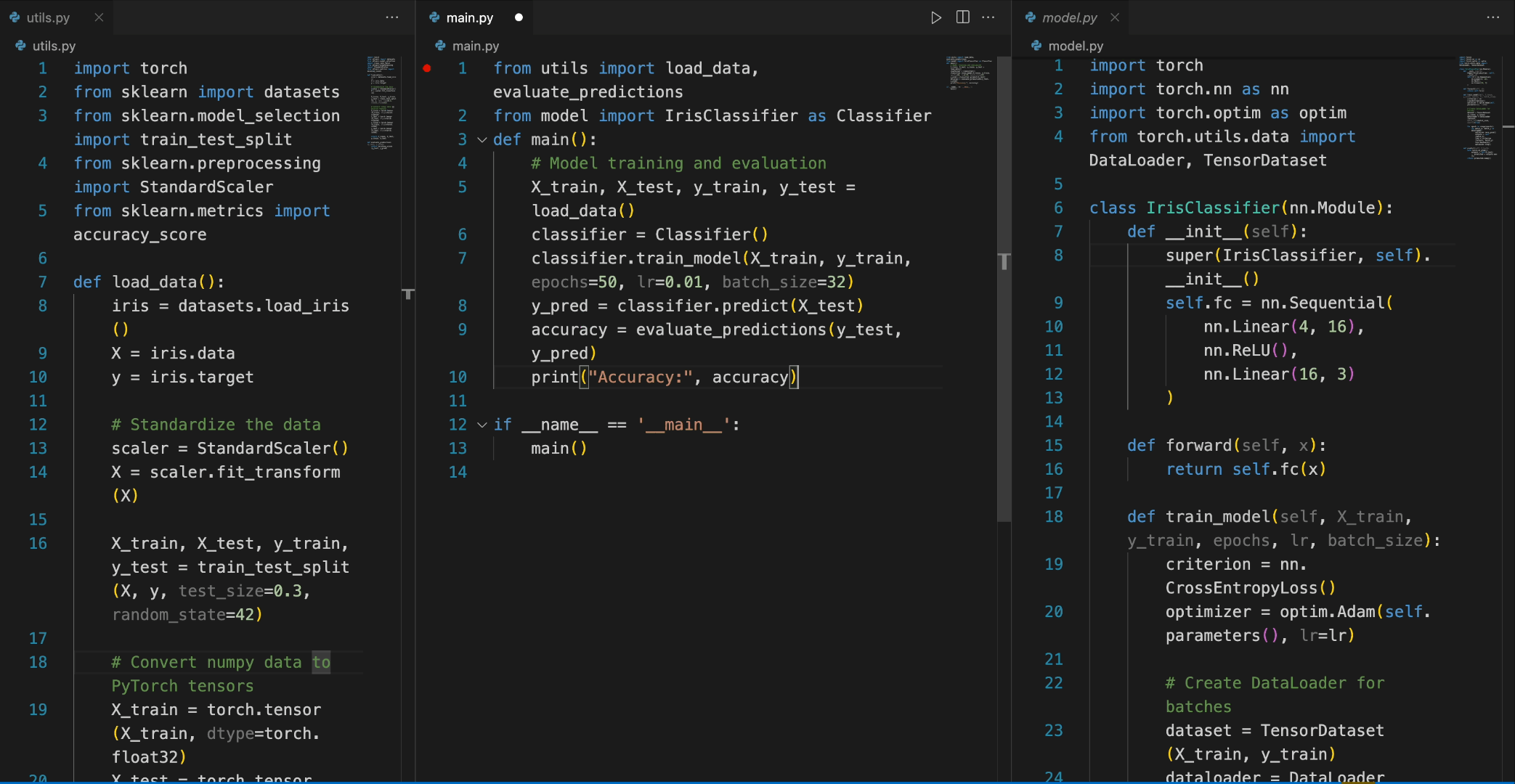
In the following scenario, the DeepSeek-Coder-6.7B model effectively calls a class **IrisClassifier** and its member function from the `model.py` file, and also utilizes functions from the `utils.py` file, to correctly complete the **main** function in the `main.py` file for model training and evaluation.
### 5. How to Fine-tune DeepSeek-Coder
We provide script `finetune/finetune_deepseekcoder.py` for users to finetune our models on downstream tasks.
The script supports the training with [DeepSpeed](https://github.com/microsoft/DeepSpeed). You need install required packages by:
```bash
pip install -r finetune/requirements.txt
```
Please follow [Sample Dataset Format](https://huggingface.co/datasets/nickrosh/Evol-Instruct-Code-80k-v1) to prepare your training data.
Each line is a json-serialized string with two required fields `instruction` and `output`.
After data preparation, you can use the sample shell script to finetune `deepseek-ai/deepseek-coder-6.7b-instruct`.
Remember to specify `DATA_PATH`, `OUTPUT_PATH`.
And please choose appropriate hyper-parameters(e.g., `learning_rate`, `per_device_train_batch_size`) according to your scenario.
```bash
DATA_PATH="
### 4. How to Use
Before proceeding, you'll need to install the necessary dependencies. You can do this by running the following command:
```
pip install -r requirements.txt
```
A demo is also available on the [🤗 Hugging Face Space](https://huggingface.co/spaces/deepseek-ai/deepseek-coder-33b-instruct), and you can run the demo locally using `app.py` in the [demo](https://github.com/deepseek-ai/deepseek-coder/tree/main/demo) folder. (Thanks to all the HF team for their support)
Here are some examples of how to use our model.
#### 1) Code Completion
```python
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM
import torch
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("deepseek-ai/deepseek-coder-6.7b-base", trust_remote_code=True)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("deepseek-ai/deepseek-coder-6.7b-base", trust_remote_code=True, torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16).cuda()
input_text = "#write a quick sort algorithm"
inputs = tokenizer(input_text, return_tensors="pt").to(model.device)
outputs = model.generate(**inputs, max_length=128)
print(tokenizer.decode(outputs[0], skip_special_tokens=True))
```
This code will output the following result:
```
def quick_sort(arr):
if len(arr) <= 1:
return arr
pivot = arr[0]
left = []
right = []
for i in range(1, len(arr)):
if arr[i] < pivot:
left.append(arr[i])
else:
right.append(arr[i])
return quick_sort(left) + [pivot] + quick_sort(right)
```
#### 2) Code Insertion
```python
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM
import torch
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("deepseek-ai/deepseek-coder-6.7b-base", trust_remote_code=True)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("deepseek-ai/deepseek-coder-6.7b-base", trust_remote_code=True, torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16).cuda()
input_text = """<|fim▁begin|>def quick_sort(arr):
if len(arr) <= 1:
return arr
pivot = arr[0]
left = []
right = []
<|fim▁hole|>
if arr[i] < pivot:
left.append(arr[i])
else:
right.append(arr[i])
return quick_sort(left) + [pivot] + quick_sort(right)<|fim▁end|>"""
inputs = tokenizer(input_text, return_tensors="pt").to(model.device)
outputs = model.generate(**inputs, max_length=128)
print(tokenizer.decode(outputs[0], skip_special_tokens=True)[len(input_text):])
```
This code will output the following result:
```
for i in range(1, len(arr)):
```
#### 3) Chat Model Inference
```python
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM
import torch
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("deepseek-ai/deepseek-coder-6.7b-instruct", trust_remote_code=True)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("deepseek-ai/deepseek-coder-6.7b-instruct", trust_remote_code=True, torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16).cuda()
messages=[
{ 'role': 'user', 'content': "write a quick sort algorithm in python."}
]
inputs = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(messages, add_generation_prompt=True, return_tensors="pt").to(model.device)
# tokenizer.eos_token_id is the id of <|EOT|> token
outputs = model.generate(inputs, max_new_tokens=512, do_sample=False, top_k=50, top_p=0.95, num_return_sequences=1, eos_token_id=tokenizer.eos_token_id)
print(tokenizer.decode(outputs[0][len(inputs[0]):], skip_special_tokens=True))
```
This code will output the following result:
```
Sure, here is a simple implementation of the Quick Sort algorithm in Python:
def quick_sort(arr):
if len(arr) <= 1:
return arr
else:
pivot = arr[0]
less_than_pivot = [x for x in arr[1:] if x <= pivot]
greater_than_pivot = [x for x in arr[1:] if x > pivot]
return quick_sort(less_than_pivot) + [pivot] + quick_sort(greater_than_pivot)
# Test the function
arr = [10, 7, 8, 9, 1, 5]
print("Original array:", arr)
print("Sorted array:", quick_sort(arr))
This code works by selecting a 'pivot' element from the array and partitioning the other elements into two sub-arrays, according to whether they are less than or greater than the pivot. The pivot element is then in its final position. The process is then repeated for the sub-arrays.
```
If you don't want to use the provided API `apply_chat_template` which loads the template from `tokenizer_config.json`, you can use the following template to chat with our model. Replace the `['content']` with your instructions and the model's previous (if any) responses, then the model will generate the response to the currently given instruction.
```
You are an AI programming assistant, utilizing the DeepSeek Coder model, developed by DeepSeek Company, and you only answer questions related to computer science. For politically sensitive questions, security and privacy issues, and other non-computer science questions, you will refuse to answer.
### Instruction:
['content']
### Response:
['content']
<|EOT|>
### Instruction:
['content']
### Response:
```
#### 4) Repository Level Code Completion
```python
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM
import torch
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("deepseek-ai/deepseek-coder-6.7b-base", trust_remote_code=True)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("deepseek-ai/deepseek-coder-6.7b-base", trust_remote_code=True, torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16).cuda()
input_text = """#utils.py
import torch
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
def load_data():
iris = datasets.load_iris()
X = iris.data
y = iris.target
# Standardize the data
scaler = StandardScaler()
X = scaler.fit_transform(X)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.3, random_state=42)
# Convert numpy data to PyTorch tensors
X_train = torch.tensor(X_train, dtype=torch.float32)
X_test = torch.tensor(X_test, dtype=torch.float32)
y_train = torch.tensor(y_train, dtype=torch.int64)
y_test = torch.tensor(y_test, dtype=torch.int64)
return X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test
def evaluate_predictions(y_test, y_pred):
return accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred)
# model.py
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader, TensorDataset
class IrisClassifier(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(IrisClassifier, self).__init__()
self.fc = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(4, 16),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(16, 3)
)
def forward(self, x):
return self.fc(x)
def train_model(self, X_train, y_train, epochs, lr, batch_size):
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = optim.Adam(self.parameters(), lr=lr)
# Create DataLoader for batches
dataset = TensorDataset(X_train, y_train)
dataloader = DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True)
for epoch in range(epochs):
for batch_X, batch_y in dataloader:
optimizer.zero_grad()
outputs = self(batch_X)
loss = criterion(outputs, batch_y)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
def predict(self, X_test):
with torch.no_grad():
outputs = self(X_test)
_, predicted = outputs.max(1)
return predicted.numpy()
# main.py
from utils import load_data, evaluate_predictions
from model import IrisClassifier as Classifier
def main():
# Model training and evaluation
"""
inputs = tokenizer(input_text, return_tensors="pt").to(model.device)
outputs = model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=140)
print(tokenizer.decode(outputs[0]))
```
---
In the following scenario, the DeepSeek-Coder-6.7B model effectively calls a class **IrisClassifier** and its member function from the `model.py` file, and also utilizes functions from the `utils.py` file, to correctly complete the **main** function in the `main.py` file for model training and evaluation.

### 5. How to Fine-tune DeepSeek-Coder
We provide script `finetune/finetune_deepseekcoder.py` for users to finetune our models on downstream tasks.
The script supports the training with [DeepSpeed](https://github.com/microsoft/DeepSpeed). You need install required packages by:
```bash
pip install -r finetune/requirements.txt
```
Please follow [Sample Dataset Format](https://huggingface.co/datasets/nickrosh/Evol-Instruct-Code-80k-v1) to prepare your training data.
Each line is a json-serialized string with two required fields `instruction` and `output`.
After data preparation, you can use the sample shell script to finetune `deepseek-ai/deepseek-coder-6.7b-instruct`.
Remember to specify `DATA_PATH`, `OUTPUT_PATH`.
And please choose appropriate hyper-parameters(e.g., `learning_rate`, `per_device_train_batch_size`) according to your scenario.
```bash
DATA_PATH="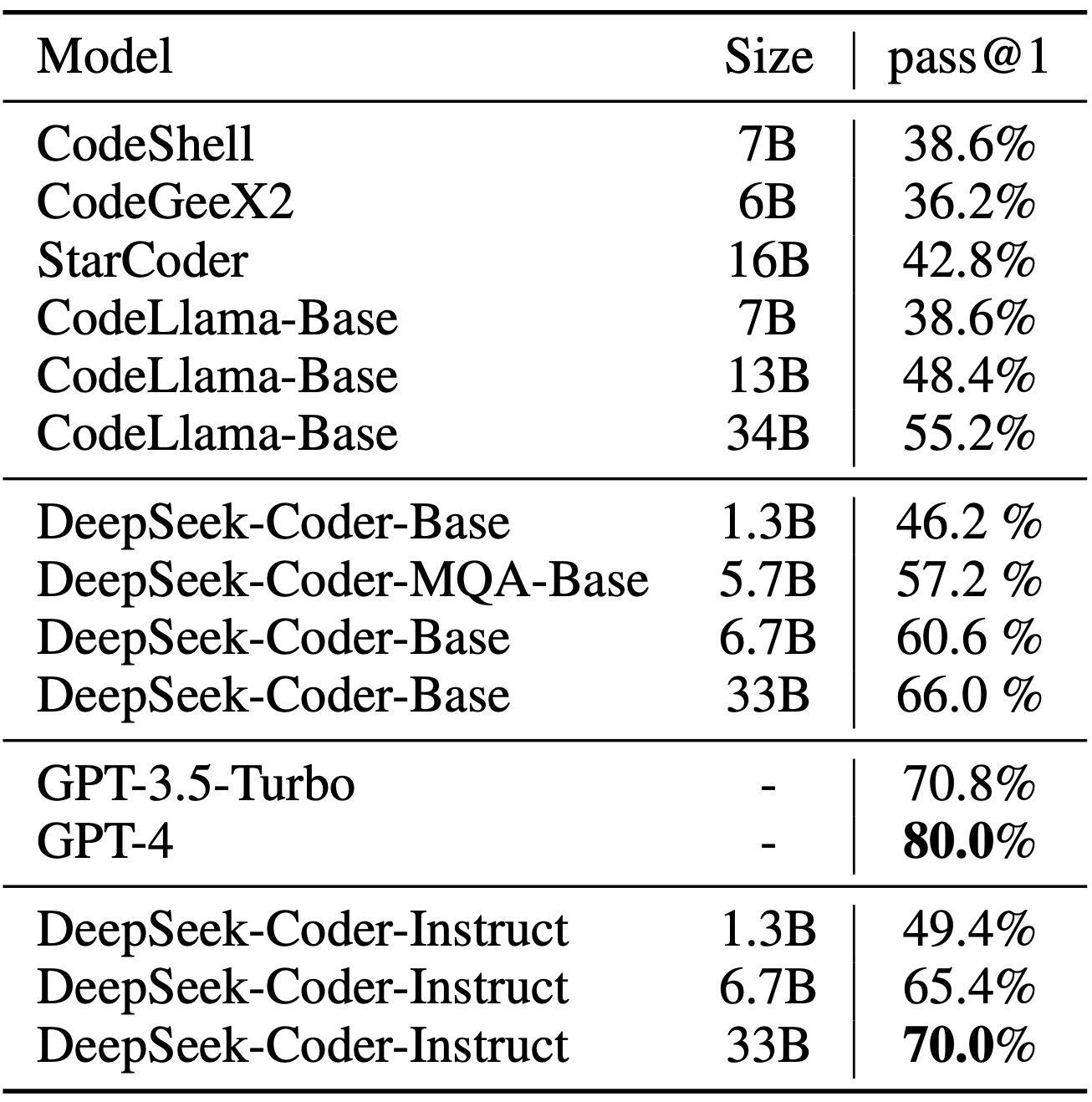 #### 3) DS-1000 Benchmark
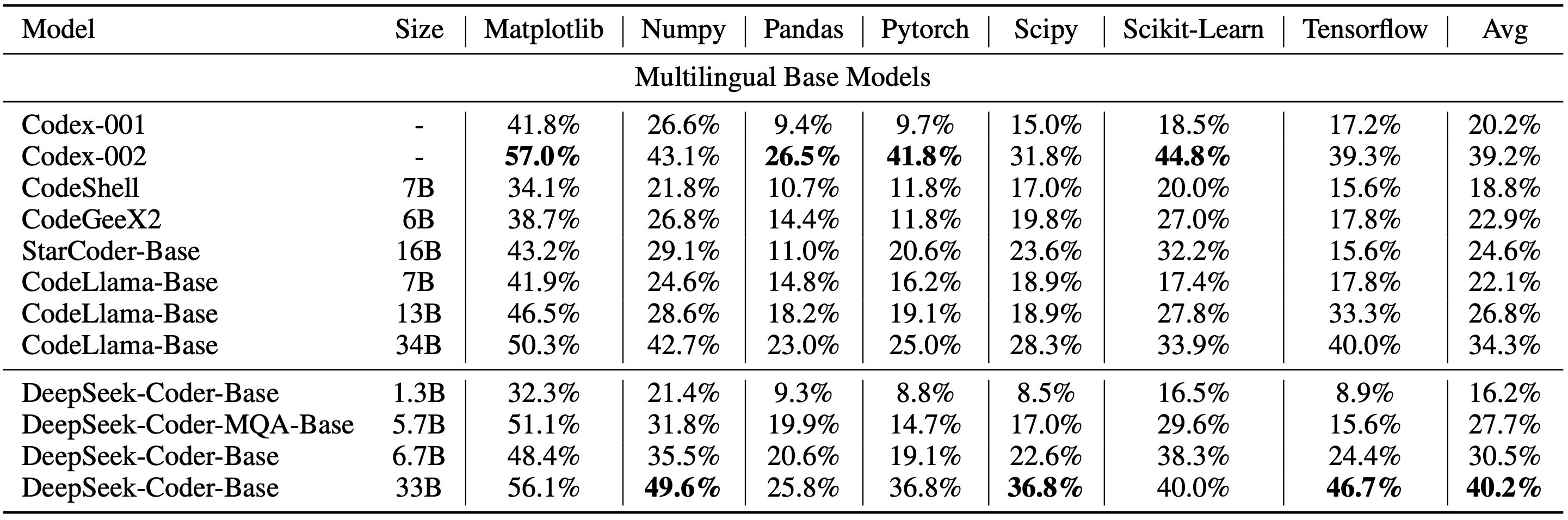
#### 4) Program-Aid Math Reasoning Benchmark
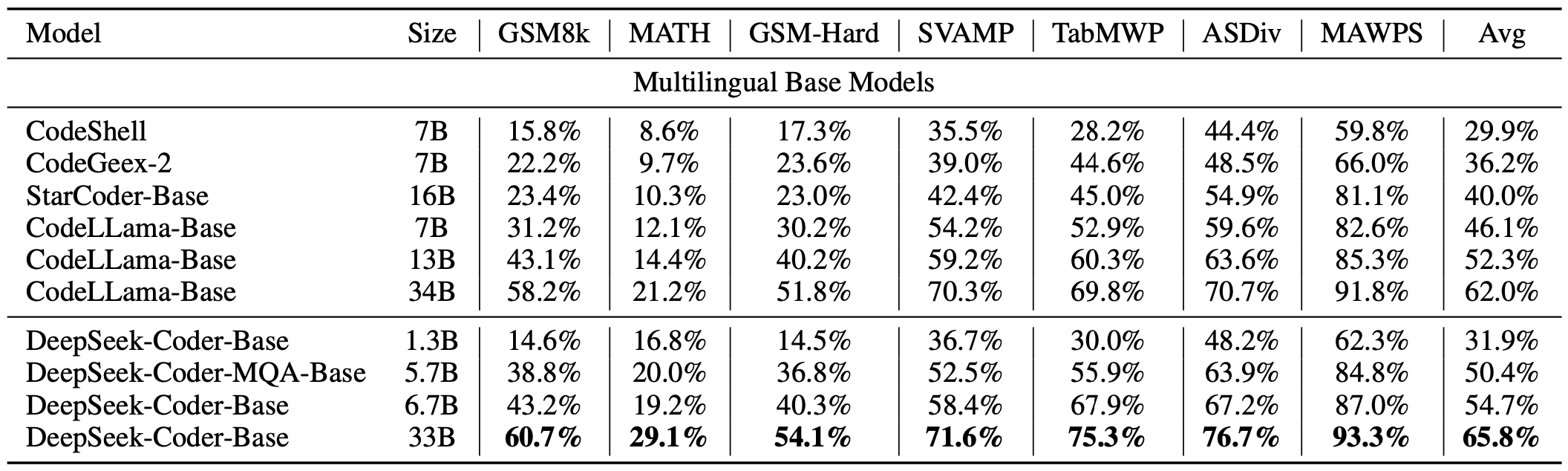
### Inference with vLLM
You can also employ [vLLM](https://github.com/vllm-project/vllm) for high-throughput inference.
**Text Completion**
```python
from vllm import LLM, SamplingParams
tp_size = 4 # Tensor Parallelism
sampling_params = SamplingParams(temperature=0.7, top_p=0.9, max_tokens=100)
model_name = "deepseek-ai/deepseek-coder-6.7b-base"
llm = LLM(model=model_name, trust_remote_code=True, gpu_memory_utilization=0.9, tensor_parallel_size=tp_size)
prompts = [
"If everyone in a country loves one another,",
"The research should also focus on the technologies",
"To determine if the label is correct, we need to"
]
outputs = llm.generate(prompts, sampling_params)
generated_text = [output.outputs[0].text for output in outputs]
print(generated_text)
```
**Chat Completion**
```python
from transformers import AutoTokenizer
from vllm import LLM, SamplingParams
tp_size = 4 # Tensor Parallelism
sampling_params = SamplingParams(temperature=0.7, top_p=0.9, max_tokens=100)
model_name = "deepseek-ai/deepseek-coder-6.7b-instruct"
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
llm = LLM(model=model_name, trust_remote_code=True, gpu_memory_utilization=0.9, tensor_parallel_size=tp_size)
messages_list = [
[{"role": "user", "content": "Who are you?"}],
[{"role": "user", "content": "What can you do?"}],
[{"role": "user", "content": "Explain Transformer briefly."}],
]
prompts = [tokenizer.apply_chat_template(messages, add_generation_prompt=True, tokenize=False) for messages in messages_list]
sampling_params.stop = [tokenizer.eos_token]
outputs = llm.generate(prompts, sampling_params)
generated_text = [output.outputs[0].text for output in outputs]
print(generated_text)
```
### 7. Q&A
#### Could You Provide the tokenizer.model File for Model Quantization?
DeepSeek Coder utilizes the [HuggingFace Tokenizer](https://huggingface.co/docs/tokenizers/index) to implement the Bytelevel-BPE algorithm, with specially designed pre-tokenizers to ensure optimal performance. Currently, there is no direct way to convert the tokenizer into a SentencePiece tokenizer. We are contributing to the open-source quantization methods facilitate the usage of HuggingFace Tokenizer.
##### GGUF(llama.cpp)
We have submitted a [PR](https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp/pull/4070) to the popular quantization repository [llama.cpp](https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp) to fully support all HuggingFace pre-tokenizers, including ours.
While waiting for the PR to be merged, you can generate your GGUF model using the following steps:
```bash
git clone https://github.com/DOGEwbx/llama.cpp.git
cd llama.cpp
git checkout regex_gpt2_preprocess
# set up the environment according to README
make
python3 -m pip install -r requirements.txt
# generate GGUF model
python convert-hf-to-gguf.py
#### 3) DS-1000 Benchmark

#### 4) Program-Aid Math Reasoning Benchmark

### Inference with vLLM
You can also employ [vLLM](https://github.com/vllm-project/vllm) for high-throughput inference.
**Text Completion**
```python
from vllm import LLM, SamplingParams
tp_size = 4 # Tensor Parallelism
sampling_params = SamplingParams(temperature=0.7, top_p=0.9, max_tokens=100)
model_name = "deepseek-ai/deepseek-coder-6.7b-base"
llm = LLM(model=model_name, trust_remote_code=True, gpu_memory_utilization=0.9, tensor_parallel_size=tp_size)
prompts = [
"If everyone in a country loves one another,",
"The research should also focus on the technologies",
"To determine if the label is correct, we need to"
]
outputs = llm.generate(prompts, sampling_params)
generated_text = [output.outputs[0].text for output in outputs]
print(generated_text)
```
**Chat Completion**
```python
from transformers import AutoTokenizer
from vllm import LLM, SamplingParams
tp_size = 4 # Tensor Parallelism
sampling_params = SamplingParams(temperature=0.7, top_p=0.9, max_tokens=100)
model_name = "deepseek-ai/deepseek-coder-6.7b-instruct"
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
llm = LLM(model=model_name, trust_remote_code=True, gpu_memory_utilization=0.9, tensor_parallel_size=tp_size)
messages_list = [
[{"role": "user", "content": "Who are you?"}],
[{"role": "user", "content": "What can you do?"}],
[{"role": "user", "content": "Explain Transformer briefly."}],
]
prompts = [tokenizer.apply_chat_template(messages, add_generation_prompt=True, tokenize=False) for messages in messages_list]
sampling_params.stop = [tokenizer.eos_token]
outputs = llm.generate(prompts, sampling_params)
generated_text = [output.outputs[0].text for output in outputs]
print(generated_text)
```
### 7. Q&A
#### Could You Provide the tokenizer.model File for Model Quantization?
DeepSeek Coder utilizes the [HuggingFace Tokenizer](https://huggingface.co/docs/tokenizers/index) to implement the Bytelevel-BPE algorithm, with specially designed pre-tokenizers to ensure optimal performance. Currently, there is no direct way to convert the tokenizer into a SentencePiece tokenizer. We are contributing to the open-source quantization methods facilitate the usage of HuggingFace Tokenizer.
##### GGUF(llama.cpp)
We have submitted a [PR](https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp/pull/4070) to the popular quantization repository [llama.cpp](https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp) to fully support all HuggingFace pre-tokenizers, including ours.
While waiting for the PR to be merged, you can generate your GGUF model using the following steps:
```bash
git clone https://github.com/DOGEwbx/llama.cpp.git
cd llama.cpp
git checkout regex_gpt2_preprocess
# set up the environment according to README
make
python3 -m pip install -r requirements.txt
# generate GGUF model
python convert-hf-to-gguf.py