---
title: Remote Execution
---
The [execute_remotely_example](https://github.com/clearml/clearml/blob/master/examples/advanced/execute_remotely_example.py)
script demonstrates the use of the [`Task.execute_remotely()`](../../references/sdk/task.md#execute_remotely) method.
:::note
Make sure to have at least one [ClearML Agent](../../clearml_agent.md) running and assigned to listen to the `default` queue:
```
clearml-agent daemon --queue default
```
:::
## Execution Flow
The script trains a simple deep neural network on the PyTorch built-in MNIST dataset. The following describes the code's
execution flow:
1. The training runs for one epoch.
1. The code uses [`Task.execute_remotely()`](../../references/sdk/task.md#execute_remotely), which terminates the local execution of the code and enqueues the task
to the `default` queue, as specified in the `queue_name` parameter.
1. An agent listening to the queue fetches the task and restarts task execution remotely. When the agent executes the task,
the `execute_remotely` is considered no-op.
An execution flow that uses `execute_remotely` is especially helpful when running code on a development machine for a few iterations
to debug and to make sure the code doesn't crash, or to set up an environment. After that, the training can be
moved to be executed by a stronger machine.
During the execution of the example script, the code does the following:
* Uses ClearML's automatic and explicit logging.
* Creates an task named `Remote_execution PyTorch MNIST train` in the `examples` project.
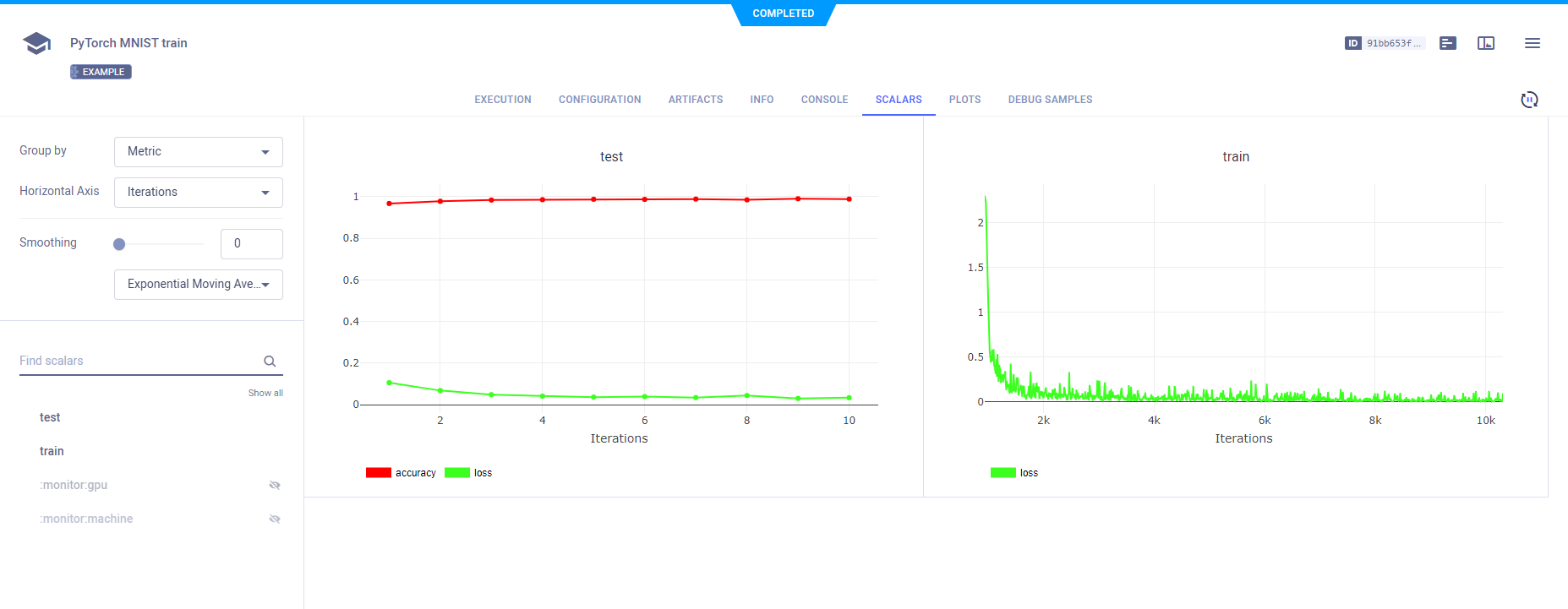
## Scalars
In the example script's `train` function, the following code explicitly reports scalars to ClearML:
```python
Logger.current_logger().report_scalar(
title="train",
series="loss",
iteration=(epoch * len(train_loader) + batch_idx),
value=loss.item()
)
```
In the script's `test` function, the code explicitly reports `loss` and `accuracy` scalars.
```python
Logger.current_logger().report_scalar(
title="test", series="loss", iteration=epoch, value=test_loss
)
Logger.current_logger().report_scalar(
title="test", series="accuracy", iteration=epoch, value=(correct / len(test_loader.dataset))
)
```
These scalars can be visualized in plots, which appear in the ClearML web UI, in the task's **SCALARS** tab.
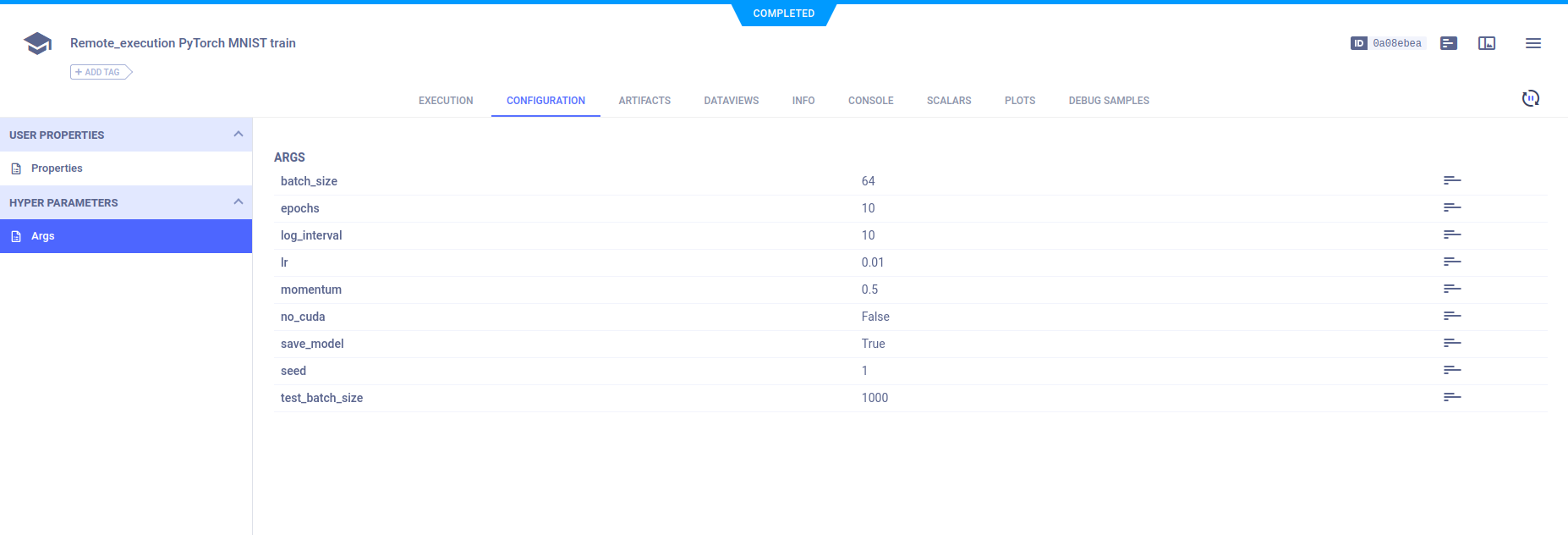
## Hyperparameters
ClearML automatically logs command line options defined with `argparse`. They appear in **CONFIGURATION** **>** **HYPERPARAMETERS** **>** **Args**.
## Console
Text printed to the console for training progress, as well as all other console output, appear in **CONSOLE**.
## Artifacts
Models created by the task appear in the task's **ARTIFACTS** tab. ClearML automatically logs and tracks models
and any snapshots created using PyTorch.